Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV) G protein-coupled receptor (vGPCR) activates the ORF50 lytic switch promoter: a potential positive feedback loop for sustained ORF50 gene expression
- PMID: 19640558
- PMCID: PMC2747482
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.07.002
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV) G protein-coupled receptor (vGPCR) activates the ORF50 lytic switch promoter: a potential positive feedback loop for sustained ORF50 gene expression
Abstract
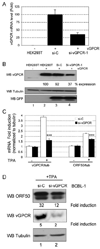
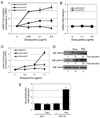
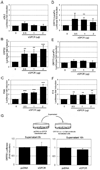
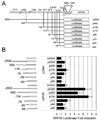
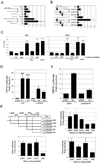
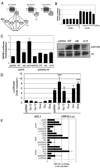
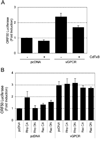
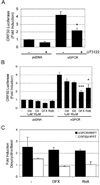
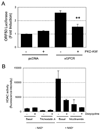
KSHV vGPCR, a lytic cycle associated protein, induces several signaling pathways leading to the activation of various transcription factors and consequently the expression of cellular and viral genes. Though the role of vGPCR in KSHV tumorigenicity has been well studied, its function related to the viral life cycle is poorly understood. Reduction in vGPCR by RNA interference also resulted in the reduction in KSHV lytic switch ORF50 gene and protein expression. Induction of vGPCR by doxycycline in BC3.14 cells also resulted in more KSHV production. When this was explored, induction of the ORF50 promoter by vGPCR expression was observed. Further examination of the molecular mechanisms by which vGPCR regulates the ORF50 promoter, using various ORF50 promoter constructs, revealed that induction of ORF50 promoter by vGPCR did not involve AP1 but was dependent on Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors. vGPCR signaling led to an increase in Sp1 and Sp3 DNA binding activity and a decrease in histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. These activities were pertussis toxin independent, did not involve Rho and Rac-GTPases and involved the heterotrimeric G protein subunits Galpha12 and Galphaq. Studies using pharmacologic inhibitors and dominant-negative proteins identified phospholipase C, the novel protein kinase C (novel PKC) family and protein kinase D (PKD) as part of the signaling initiated by vGPCR leading to ORF50 promoter activation. Taken together, this study suggests a role for vGPCR in the sustained expression of ORF50 which could lead to a continued activation of lytic cycle genes and ultimately to successful viral progeny formation.
Figures
References
-
- Alberts BLJ, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Molecular biology of the cell. 2002
-
- Bais C, Van Geelen A, Eroles P, Mutlu A, Chiozzini C, Dias S, Silverstein RL, Rafii S, Mesri EA. Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor immortalizes human endothelial cells by activation of the VEGF receptor-2/ KDR. Cancer Cell. 2003;3(2):131–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

