Mechanisms of catalysis and inhibition operative in the arginine deiminase from the human pathogen Giardia lamblia
- PMID: 19640561
- PMCID: PMC4590290
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2009.06.001
Mechanisms of catalysis and inhibition operative in the arginine deiminase from the human pathogen Giardia lamblia
Abstract
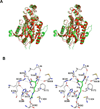
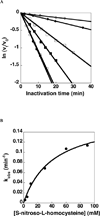
Giardia lamblia arginine deiminase (GlAD), the topic of this paper, belongs to the hydrolase branch of the guanidine-modifying enzyme superfamily, whose members employ Cys-mediated nucleophilic catalysis to promote deimination of l-arginine and its naturally occurring derivatives. G. lamblia is the causative agent in the human disease giardiasis. The results of RNAi/antisense RNA gene-silencing studies reported herein indicate that GlAD is essential for G. lamblia trophozoite survival and thus, a potential target for the development of therapeutic agents for the treatment of giardiasis. The homodimeric recombinant protein was prepared in Escherichia coli for in-depth biochemical characterization. The 2-domain GlAD monomer consists of a N-terminal domain that shares an active site structure (depicted by an insilico model) and kinetic properties (determined by steady-state and transient state kinetic analysis) with its bacterial AD counterparts, and a C-terminal domain of unknown fold and function. GlAD was found to be active over a wide pH range and to accept l-arginine, l-arginine ethyl ester, N(alpha)-benzoyl-l-arginine, and N(omega)-amino-l-arginine as substrates but not agmatine, l-homoarginine, N(alpha)-benzoyl-l-arginine ethyl ester or a variety of arginine-containing peptides. The intermediacy of a Cys424-alkylthiouronium ion covalent enzyme adduct was demonstrated and the rate constants for formation (k(1)=80s(-1)) and hydrolysis (k(2)=35s(-1)) of the intermediate were determined. The comparatively lower value of the steady-state rate constant (k(cat)=2.6s(-1)), suggests that a step following citrulline formation is rate-limiting. Inhibition of GlAD using Cys directed agents was briefly explored. S-Nitroso-l-homocysteine was shown to be an active site directed, irreversible inhibitor whereas N(omega)-cyano-l-arginine did not inhibit GlAD but instead proved to be an active site directed, irreversible inhibitor of the Bacillus cereus AD.
Figures









References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

