Feedback control of the EGFR signaling gradient: superposition of domain-splitting events in Drosophila oogenesis
- PMID: 19641013
- PMCID: PMC2723063
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.039545
Feedback control of the EGFR signaling gradient: superposition of domain-splitting events in Drosophila oogenesis
Abstract
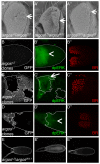
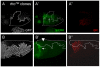
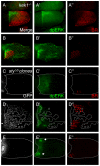
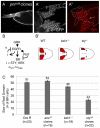
The morphogenesis of structures with repeated functional units, such as body segments and appendages, depends on multi-domain patterns of cell signaling and gene expression. We demonstrate that during Drosophila oogenesis, the two-domain expression pattern of Broad, a transcription factor essential for the formation of the two respiratory eggshell appendages, is established by a single gradient of EGFR activation that induces both Broad and Pointed, which mediates repression of Broad. Two negative-feedback loops provided by the intracellular inhibitors of EGFR signaling, Kekkon-1 and Sprouty, control the number and position of Broad-expressing cells and in this way influence eggshell morphology. Later in oogenesis, the gradient of EGFR activation is split into two smaller domains in a process that depends on Argos, a secreted antagonist of EGFR signaling. In contrast to the previously proposed model of eggshell patterning, we show that the two-domain pattern of EGFR signaling is not essential for specifying the number of appendages. Thus, the processes that define the two-domain patterns of Broad and EGFR activation are distinct; their actions are separated in time and have different effects on eggshell morphology.
Figures


References
-
- Atkey, M. R., Lachance, J. F., Walczak, M., Rebello, T. and Nilson, L. A. (2006). Capicua regulates follicle cell fate in the Drosophila ovary through repression of mirror. Development 133, 2115-2123. - PubMed
-
- Berg, C. A. (2005). The Drosophila shell game: patterning genes and morphological change. Trends Genet. 21, 346-355. - PubMed
-
- Bier, E., Jan, L. Y. and Jan, Y. N. (1990). rhomboid, a gene required for dorsoventral axis establishment and peripheral nervous system development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 4, 190-203. - PubMed
-
- Boisclair Lachance, J.-F., Fregoso Lomas, M., Eleiche, A., Bouchard Kerr, P. and Nilson, L. A. (2009). Graded Egfr activity patterns the Drosophila eggshell independently of autocrine feedback. Development 136, 2893-2902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

