Mutations in UDP-Glucose:sterol glucosyltransferase in Arabidopsis cause transparent testa phenotype and suberization defect in seeds
- PMID: 19641030
- PMCID: PMC2735980
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.140582
Mutations in UDP-Glucose:sterol glucosyltransferase in Arabidopsis cause transparent testa phenotype and suberization defect in seeds
Abstract
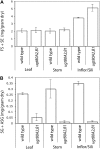
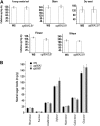
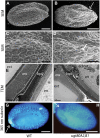
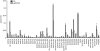
In higher plants, the most abundant sterol derivatives are steryl glycosides (SGs) and acyl SGs. Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) contains two genes, UGT80A2 and UGT80B1, that encode UDP-Glc:sterol glycosyltransferases, enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of SGs. Lines having mutations in UGT80A2, UGT80B1, or both UGT80A2 and UGT8B1 were identified and characterized. The ugt80A2 lines were viable and exhibited relatively minor effects on plant growth. Conversely, ugt80B1 mutants displayed an array of phenotypes that were pronounced in the embryo and seed. Most notable was the finding that ugt80B1 was allelic to transparent testa15 and displayed a transparent testa phenotype and a reduction in seed size. In addition to the role of UGT80B1 in the deposition of flavanoids, a loss of suberization of the seed was apparent in ugt80B1 by the lack of autofluorescence at the hilum region. Moreover, in ugt80B1, scanning and transmission electron microscopy reveals that the outer integument of the seed coat lost the electron-dense cuticle layer at its surface and displayed altered cell morphology. Gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry of lipid polyester monomers confirmed a drastic decrease in aliphatic suberin and cutin-like polymers that was associated with an inability to limit tetrazolium salt uptake. The findings suggest a membrane function for SGs and acyl SGs in trafficking of lipid polyester precursors. An ancillary observation was that cellulose biosynthesis was unaffected in the double mutant, inconsistent with a predicted role for SGs in priming cellulose synthesis.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham W, Wertz PW, Burken RR, Downing DT (1987) Glucosylsterol and acylglucosylsterol of snake epidermis: structure determination. J Lipid Res 28 446–449 - PubMed
-
- Baxter IR, Young JC, Armstrong G, Foster N, Bogenschutz N, Cordova T, Peer WA, Hazen SP, Murphy AS, Harper JF (2005) A plasma membrane H+-ATPase is required for the formation of proanthocyanidins in the seed coat endothelium of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102 2649–2654 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blumenkranz N, Asboe-Hanson G (1973) New methods for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54 484–489 - PubMed
-
- Bouvier-Nave P, Ullmann P, Rimmele D, Benveniste P (1984) Phospholipid dependence of plant UDP-glucose sterol β-D-glucosyl transferase. I. Detergent mediated delipidation by selective solubilization. Plant Sci Lett 36 19–27
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

