Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant VP2 capsids for the detection of antibodies to Aleutian mink disease virus
- PMID: 19641102
- PMCID: PMC2745009
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00148-09
Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant VP2 capsids for the detection of antibodies to Aleutian mink disease virus
Abstract
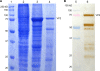
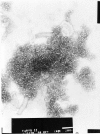
Aleutian disease (AD), a common infectious disease in farmed minks worldwide, is caused by Aleutian mink disease virus (AMDV). Serodiagnosis of AD in minks has been based on detection of AMDV antibodies by counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE) since the 1980s. The aim of this study was to develop and evaluate an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on recombinant virus-like particles (VLPs) for identifying AMDV antibodies from mink sera. AMDV capsid protein (VP2) of a Finnish wild-type strain was expressed by the baculovirus system in Spodoptera frugiperda 9 insect cells and was shown to self-assemble to VLPs (with an ultrastructure similar to that of the actual virion). A direct immunoglobulin G ELISA was established using purified recombinant AMDV VP2 VLPs as an antigen. Sera from farmed minks were collected to evaluate the AMDV VP2 ELISA (n = 316) and CIE (n = 209) based on AMDV VP2 recombinant antigen in parallel with CIE performed using a commercially available traditional antigen. CIE performed with the recombinant antigen had a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and ELISA a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 97%, with reference to CIE performed with the commercial antigen. The results show that the recombinant AMDV VP2 VLPs are antigenic and that AMDV VP2 ELISA is sensitive and specific and encourage further development of the method for high-throughput diagnostics, involving hundreds of thousands of samples in Finland annually.
Figures

References
-
- Aasted, B., and A. Cohn. 1982. Inhibition of precipitation in counter current electrophoresis. A sensitive method for detection of mink antibodies to Aleutian disease virus. APMIS Sect. C 90:15-19. - PubMed
-
- Aasted, B., S. Alexandersen, and J. Christensen. 1998. Vaccination with Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (AMDV) capsid proteins enhances disease, while vaccination with the major non-structural protein causes partial protection from disease. Vaccine 16:1158-1165. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersen, S., and J. Hau. 1985. Rocket line immunoelectrophoresis: an improved assay for simultaneous quantification of mink parvovirus (Aleutian disease virus) antigen and antibody. J. Virol. Methods 10:145-151. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersen, S., J. Hau, B. Aasted, and O. M. Poulsen. 1985. Thin-layer counter current line absorption immunoelectrophoretic analysis of antigens and antibodies to Aleutian disease virus—a mink parvovirus. Electrophoresis 6:535-538.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

