Pore architecture and ion sites in acid-sensing ion channels and P2X receptors
- PMID: 19641589
- PMCID: PMC2845979
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08218
Pore architecture and ion sites in acid-sensing ion channels and P2X receptors
Abstract
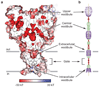
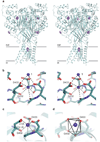
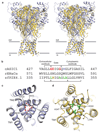
Acid-sensing ion channels are proton-activated, sodium-selective channels composed of three subunits, and are members of the superfamily of epithelial sodium channels, mechanosensitive and FMRF-amide peptide-gated ion channels. These ubiquitous eukaryotic ion channels have essential roles in biological activities as diverse as sodium homeostasis, taste and pain. Despite their crucial roles in biology and their unusual trimeric subunit stoichiometry, there is little knowledge of the structural and chemical principles underlying their ion channel architecture and ion-binding sites. Here we present the structure of a functional acid-sensing ion channel in a desensitized state at 3 A resolution, the location and composition of the approximately 8 A 'thick' desensitization gate, and the trigonal antiprism coordination of caesium ions bound in the extracellular vestibule. Comparison of the acid-sensing ion channel structure with the ATP-gated P2X(4) receptor reveals similarity in pore architecture and aqueous vestibules, suggesting that there are unanticipated yet common structural and mechanistic principles.
Figures


Comment in
-
Structural biology: Trimeric ion-channel design.Nature. 2009 Jul 30;460(7255):580-1. doi: 10.1038/460580a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19641581 No abstract available.
References
-
- Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M. A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature. 1997;386:173–177. - PubMed
-
- Coric T, Passamaneck YJ, Zhang P, Di Gregorio A, Canessa CM. Simple chordates exhibit a proton-independent function of acid-sensing ion channels. FASEB J. 2008;22:1914–1923. - PubMed
-
- Kellenberger S, Schild L. Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:735–767. - PubMed
-
- Hesselager M, Timmermann DB, Ahring PK. pH Dependency and desensitization kinetics of heterologously expressed combinations of acid-sensing ion channel subunits. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:11006–11015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

