Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety
- PMID: 19643124
- PMCID: PMC2771628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.07.009
Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety
Abstract
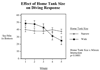
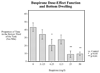
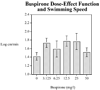
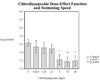
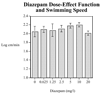
Zebrafish are becoming more widely used to study neurobehavioral pharmacology. We have developed a method to assess novel environment diving behavior of zebrafish as a model of stress response and anxiolytic drug effects. In a novel tank, zebrafish dwell in the bottom of the tank initially and then increase their swimming exploration to higher levels over time. We previously found that nicotine, which has anxiolytic effects in rodents and humans, significantly lessens the novel tank diving response in zebrafish. The specificity of the diving effect was validated with a novel vs. non-novel test tank. The novel tank diving response of zebrafish was tested when given three anxiolytic drugs from two different chemical and pharmacological classes: buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam. When the test tank was novel the diving response was clearly seen whereas it was significantly reduced when the test tank was not novel. Buspirone, a serotonergic (5HT(1A) receptor agonist) anxiolytic drug with some D(2) dopaminergic effect, had a pronounced anxiolytic-like effect in the zebrafish diving model at doses that did not have sedative effects. In contrast, chlordiazepoxide, a benzodiazepine anxiolytic drug, which is an effective agonist at GABA-A receptors, did not produce signs of anxiolysis in zebrafish over a broad dose range up to those that caused sedation. Diazepam another benzodiazepine anxiolytic drug did produce an anxiolytic effect at doses that did not cause sedation. The zebrafish novel tank diving task can be useful in discriminating anxiolytic drugs of several classes (serotonergic, benzodiazepines and nicotinic).
Figures




References
-
- Anzelius M, Ekstrom P, Mohler H, Richards JG. Immunocytochemical localization of GABAA receptor beta 2/beta 3-subunits in the brain of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L) Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 1995;8:207–221. - PubMed
-
- Anzelius M, Ekstrom P, Mohler H, Richards JG. Immunocytochemical localization of the GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor beta 2/beta 3 subunits in the optic tectum of the salmon. Journal of Receptor & Signal Transduction Research. 1995;15:413–425. - PubMed
-
- Arthur D, Levin ED. Spatial and non-spatial discrimination learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio) Animal Cognition. 2001;4:125–131.
-
- Bass SL, Gerlai R. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) responds differentially to stimulus fish: the effects of sympatric and allopatric predators and harmless fish. Behavioural Brain Research. 2008;186:107–117. - PubMed

