Electrospun silk biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine
- PMID: 19643154
- PMCID: PMC2774469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.07.005
Electrospun silk biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine
Abstract
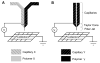
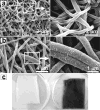
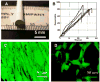
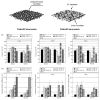
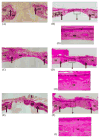
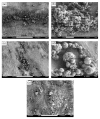
Electrospinning is a versatile technique that enables the development of nanofiber-based biomaterial scaffolds. Scaffolds can be generated that are useful for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine since they mimic the nanoscale properties of certain fibrous components of the native extracellular matrix in tissues. Silk is a natural protein with excellent biocompatibility, remarkable mechanical properties as well as tailorable degradability. Integrating these protein polymer advantages with electrospinning results in scaffolds with combined biochemical, topographical and mechanical cues with versatility for a range of biomaterial, cell and tissue studies and applications. This review covers research related to electrospinning of silk, including process parameters, post treatment of the spun fibers, functionalization of nanofibers, and the potential applications for these material systems in regenerative medicine. Research challenges and future trends are also discussed.
Figures
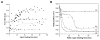


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms and control of silk-based electrospinning.Biomacromolecules. 2012 Mar 12;13(3):798-804. doi: 10.1021/bm201719s. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Biomacromolecules. 2012. PMID: 22300335 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying the mechanical properties of silk nanofiber scaffold by knitted orientation for regenerative medicine applications.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Aug 31;62(10):16-25. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016. PMID: 27609469
-
Biomimetic electrospun nanofibers for tissue regeneration.Biomed Mater. 2006 Sep;1(3):R45-53. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/1/3/R01. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Biomed Mater. 2006. PMID: 18458387 Review.
-
Electrospinning of collagen/biopolymers for regenerative medicine and cardiovascular tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009 Oct 5;61(12):1007-19. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.07.012. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009. PMID: 19651166 Review.
-
Cell-matrix mechanical interaction in electrospun polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering: Implications for scaffold design and performance.Acta Biomater. 2017 Mar 1;50:41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.12.034. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28011142 Review.
Cited by
-
Silk constructs for delivery of musculoskeletal therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Sep;64(12):1111-22. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.03.016. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22522139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of post-treatment with 75% (v/v) ethanol vapor on the properties of SF/P(LLA-CL) nanofibrous scaffolds.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2):2036-2047. doi: 10.3390/ijms13022036. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408436 Free PMC article.
-
Silk fibroin and silk-based biomaterial derivatives for ideal wound dressings.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Dec 1;164:4613-4627. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.041. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32814099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Silk Fibroin as a Persuasive Biomaterial for Bone Tissue Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2660. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032660. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging technologies in medical applications of minimum volume vitrification.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011 Aug;6(6):1115-29. doi: 10.2217/nnm.11.71. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21955080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skalak R, Fox CF, editors. Tissue engineering. Alan R Liss, Inc; New York:
-
- Vacanti JP, Vacanti CA. The challenge of tissue engineering. In: Lanza R, Langer R, Chick W, editors. Principles of Tissue Engineering. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 1997. pp. 1–5.
-
- Koh CJ, Atala A. Tissue engineering, stem cells, and cloning: opportunities for regenerative medicine. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1113–1125. - PubMed
-
- Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260:920–926. - PubMed
-
- Hoerstrup SP, Vacanti JP. Overview of tissue engineering. In: Ratner BD, Hoffman AS, Schoen FJ, editors. Biomaterial Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine. 2. Elsvier Academic Pr; 2004. pp. 712–727.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

