Urinary peptidome may predict renal function decline in type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria
- PMID: 19643930
- PMCID: PMC2736765
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008121233
Urinary peptidome may predict renal function decline in type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria
Abstract
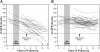
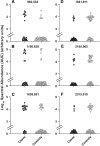
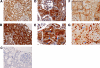
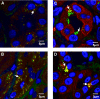
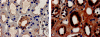
One third of patients with type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria experience an early, progressive decline in renal function that leads to advanced stages of chronic kidney disease and ESRD. We hypothesized that the urinary proteome may distinguish between stable renal function and early renal function decline among patients with type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria. We followed patients with normal renal function and microalbuminuria for 10 to 12 yr and classified them into case patients (n = 21) with progressive early renal function decline and control subjects (n = 40) with stable renal function. Using liquid chromatography matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, we identified three peptides that decreased in the urine of patients with early renal function decline [fragments of alpha1(IV) and alpha1(V) collagens and tenascin-X] and three peptides that increased (fragments of inositol pentakisphosphate 2-kinase, zona occludens 3, and FAT tumor suppressor 2). In renal biopsies from patients with early nephropathy from type 1 diabetes, we observed increased expression of inositol pentakisphosphate 2-kinase, which was present in granule-like cytoplasmic structures, and zona occludens 3. These results indicate that urinary peptide fragments reflect changes in expression of intact protein in the kidney, suggesting new potential mediators of diabetic nephropathy and candidate biomarkers for progressive renal function decline.
Figures

References
-
- Viberti GC, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Argyropoulos A, Mahmud U, Keen H:Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1: 1430–1432, 1982 - PubMed
-
- Mogensen CE, Keane WF, Bennett PH, Jerums G, Parving HH, Passa P, Steffes MW, Striker GE, Viberti GC:Prevention of diabetic renal disease with special reference to microalbuminuria. Lancet 346: 1080–1084, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Perkins BA, Ficociello LH, Silva KH, Finkelstein DM, Warram JH, Krolewski AS:Regression of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 348: 2285–2293, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Giorgino F, Laviola L, Cavallo Perin P, Solnica B, Fuller J, Chaturvedi N:Factors associated with progression to macroalbuminuria in microalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients: The EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study. Diabetologia 47: 1020–1028, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Araki S, Haneda M, Sugimoto T, Isono M, Isshiki K, Kashiwagi A, Koya D:Factors associated with frequent remission of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54: 2983–2987, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

