The structure of myostatin:follistatin 288: insights into receptor utilization and heparin binding
- PMID: 19644449
- PMCID: PMC2738701
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.205
The structure of myostatin:follistatin 288: insights into receptor utilization and heparin binding
Abstract
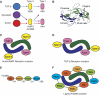
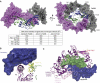
Myostatin is a member of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) family and a strong negative regulator of muscle growth. Here, we present the crystal structure of myostatin in complex with the antagonist follistatin 288 (Fst288). We find that the prehelix region of myostatin very closely resembles that of TGF-beta class members and that this region alone can be swapped into activin A to confer signalling through the non-canonical type I receptor Alk5. Furthermore, the N-terminal domain of Fst288 undergoes conformational rearrangements to bind myostatin and likely acts as a site of specificity for the antagonist. In addition, a unique continuous electropositive surface is created when myostatin binds Fst288, which significantly increases the affinity for heparin. This translates into stronger interactions with the cell surface and enhanced myostatin degradation in the presence of either Fst288 or Fst315. Overall, we have identified several characteristics unique to myostatin that will be paramount to the rational design of myostatin inhibitors that could be used in the treatment of muscle-wasting disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Allendorph GP, Isaacs MJ, Kawakami Y, Belmonte JC, Choe S (2007) BMP-3 and BMP-6 structures illuminate the nature of binding specificity with receptors. Biochemistry 46: 12238–12247 - PubMed
-
- Amthor H, Nicholas G, McKinnell I, Kemp CF, Sharma M, Kambadur R, Patel K (2004) Follistatin complexes myostatin and antagonises myostatin-mediated inhibition of myogenesis. Dev Biol 270: 19–30 - PubMed
-
- Attisano L, Carcamo J, Ventura F, Weis FM, Massague J, Wrana JL (1993) Identification of human activin and TGF β type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors. Cell 75: 671–680 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

