Expression and regulation of soluble epoxide hydrolase in adipose tissue
- PMID: 19644452
- PMCID: PMC2864128
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2009.227
Expression and regulation of soluble epoxide hydrolase in adipose tissue
Abstract
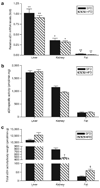
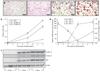
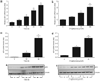
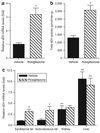
Obesity is an increasingly important public health issue reaching epidemic proportions. Visceral obesity has been defined as an important element of the metabolic syndrome and expansion of the visceral fat mass has been shown to contribute to the development of insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. To identify novel contributors to cardiovascular and metabolic abnormalities in obesity, we analyzed the adipose proteome and identified soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in the epididymal fat pad from C57BL/6J mice that received either a regular diet or a "western diet." sEH was synthesized in adipocytes and expression levels increased upon differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Although normalized sEH mRNA and protein levels did not differ in the fat pads from mice receiving a regular or a "western diet," total adipose sEH activity was higher in the obese mice, even after normalization for body weight. Furthermore, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) agonists increased the expression of sEH in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes in vitro and in adipose tissue in vivo. Considering the established role for sEH in inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, and lipid metabolism, and the suggested involvement of sEH in the development of type 2 diabetes, our study has identified adipose sEH as a potential novel therapeutic target that might affect the development of metabolic and cardiovascular abnormalities in obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Smyth S, Heron A. Diabetes and obesity: the twin epidemics. Nat Med. 2006;12:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Katagiri H, Yamada T, Oka Y. Adiposity and cardiovascular disorders: disturbance of the regulatory system consisting of humoral and neuronal signals. Circ Res. 2007;101:27–39. - PubMed
-
- Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2006;113:898–918. - PubMed
-
- Enayetallah AE, French RA, Thibodeau MS, Grant DF. Distribution of soluble epoxide hydrolase and of cytochrome P450 2C8, 2C9, and 2J2 in human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 2004;52:447–454. - PubMed
-
- Yu Z, Davis BB, Morisseau C, et al. Vascular localization of soluble epoxide hydrolase in the human kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004;286:F720–F726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

