Efficient molecular genetic diagnosis of enlarged vestibular aqueducts in East Asians
- PMID: 19645628
- PMCID: PMC2953255
- DOI: 10.1089/gtmb.2009.0054
Efficient molecular genetic diagnosis of enlarged vestibular aqueducts in East Asians
Abstract
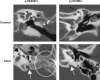
Context: Enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct (EVA) is a commonly detected inner ear anomaly related to hearing loss and often associated with mutations of SLC26A4 encoding pendrin, a transmembrane exchanger of Cl(-), I(-), and HCO(3)(-). Here we describe the phenotypes of 27 Korean EVA subjects and their SLC26A4 genotypes determined by bidirectional nucleotide sequencing.
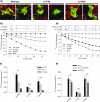
Results: The detected variants include two novel missense substitutions (p.V138L and p.P542R). We characterized the ability of p.V138L and p.P542R pendrin products to traffic to the plasma membrane in COS-7 cells and to transport Cl(-), I(-), and HCO(3)(-) in Xenopus oocytes. The results indicate that p.P542R is a benign polymorphic variant, whereas p.V138L is a pathogenic mutation. Since this and other studies of East Asian EVA cohorts show that the majority of SLC26A4 mutations affect either or both of two amplicons (exons 7-8 and 19), we developed a hierarchical protocol that integrates direct sequencing with denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography analyses for detection of SLC26A4 mutations in these populations. We validated the cost efficiency of the integrated protocol by a simulated screen of published East Asian EVA cohorts with known SLC26A4 genotypes.
Conclusions: Our study further defines the spectrum of SLC26A4 mutations among East Asians and demonstrates a rapid and efficient protocol for their detection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypo-functional SLC26A4 variants associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss and enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct: genotype-phenotype correlation or coincidental polymorphisms?Hum Mutat. 2009 Apr;30(4):599-608. doi: 10.1002/humu.20884. Hum Mutat. 2009. PMID: 19204907 Free PMC article.
-
Novel genetic determinants contribute to hearing loss in a central European cohort with enlarged vestibular aqueduct.Mol Med. 2025 Mar 22;31(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01159-9. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40121402 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel functional null allele of SLC26A4 associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct and its possible implication.Audiol Neurootol. 2014;19(5):319-26. doi: 10.1159/000366190. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Audiol Neurootol. 2014. PMID: 25358692
-
Molecular and functional characterization of human pendrin and its allelic variants.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28(3):451-66. doi: 10.1159/000335107. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 22116358 Review.
-
Hereditary hearing loss with thyroid abnormalities.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;70:43-49. doi: 10.1159/000322469. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011. PMID: 21358184 Review.
Cited by
-
Extremely discrepant mutation spectrum of SLC26A4 between Chinese patients with isolated Mondini deformity and enlarged vestibular aqueduct.J Transl Med. 2011 Sep 30;9:167. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-167. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21961810 Free PMC article.
-
An effective screening strategy for deafness in combination with a next-generation sequencing platform: a consecutive analysis.J Hum Genet. 2016 Mar;61(3):253-61. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2015.143. Epub 2016 Jan 14. J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 26763877 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a Flexible Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Platform for Detecting Prevalent Deafness Mutations Associated with Variable Degree of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Koreans.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 1;11(9):e0161756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161756. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27583405 Free PMC article.
-
[Difference of SLC26A4 gene mutation frequency between patients with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome and/or Mondini dysplasia].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Oct;35(10):891-895. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.10.006. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34628810 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Application of next generation sequencing upon the molecular genetic diagnosis of deafness.Korean J Audiol. 2012 Apr;16(1):1-5. doi: 10.7874/kja.2012.16.1.1. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Korean J Audiol. 2012. PMID: 24653861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albert S. Blons H. Jonard L, et al. SLC26A4 gene is frequently involved in nonsyndromic hearing impairment with enlarged vestibular aqueduct in Caucasian populations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14:773–779. - PubMed
-
- Borck G. Roth C. Martine U, et al. Mutations in the PDS gene in German families with Pendred's syndrome: V138F is a founder mutation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:2916–2921. - PubMed
-
- Campbell C. Cucci RA. Prasad S, et al. Pendred syndrome, DFNB4, and PDS/SLC26A4 identification of eight novel mutations and possible genotype-phenotype correlations. Hum Mutat. 2001;17:403–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

