Antinociceptive effects of NCX-701 (nitro-paracetamol) in neuropathic rats: enhancement of antinociception by co-administration with gabapentin
- PMID: 19645711
- PMCID: PMC2757700
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00343.x
Antinociceptive effects of NCX-701 (nitro-paracetamol) in neuropathic rats: enhancement of antinociception by co-administration with gabapentin
Abstract
Background and purpose: Neuropathic pain is characterized by a poor response to classic analgesics. In the present study, we have assessed the antinociceptive activity of NCX-701 (nitro-paracetamol) in neuropathic rats, after systemic and intrathecal (i.t.) administration. In addition, we analysed the possible benefit of the combination of NCX-701 and gabapentin, a well-known potent analgesic, in the treatment of neuropathic pain.
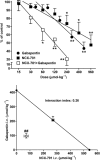
Experimental approach: The antinociceptive effects of i.v. and i.t. NCX-701 and paracetamol were studied in spinal cord neuronal responses from neuropathic adult male Wistar rats, using the recording of single motor units technique. The effect of i.v. and i.t. NCX-701 in combination with i.v. gabapentin was studied by isobolographic analysis.
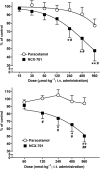
Key results: The experiments showed that NCX-701, but not paracetamol, dose-dependently reduced the nociceptive responses evoked by noxious mechanical and electrical stimulation, after i.v. (ID(50) 542 +/- 5 micromol kg(-1) for noxious mechanical stimulation) or i.t. (ID(50) 932 +/- 16 nmol kg(-1)) administration. The combined administration of i.v. or i.t. NCX-701 and i.v. gabapentin induced a more intense antinociceptive effect than any of the two drugs given alone. The isobolographic analysis showed a synergistic effect.
Conclusions and implications: NCX-701 is an effective antinociceptive compound in situations of neuropathy-induced sensitization, with an action mainly located in the spinal cord. The combination of NCX-701 and gabapentin induces a synergistic enhancement of the depression of nociceptive responses evoked by natural noxious stimulation. The use of NCX-701 alone or in combination with gabapentin might open up new and promising perspectives in the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Figures


References
-
- Bannwarth B, Netter P, Pourel J, Royer RJ, Gaucher A. Clinical pharmacokinetics of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cerebrospinal fluid. Biomed Pharmacother. 1989;43:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Barraco RA, Marcantonio DR, Phillis JW, Campbell WR. The effects of parenteral injections of adenosine and its analogs on blood pressure and heart rate in the rat. Gen Pharmacol. 1987;18:405–416. - PubMed
-
- Curros-Criado MM, Herrero JF. The antinociceptive effects of the systemic adenosine A1 receptor agonist CPA in the absence and in the presence of spinal cord sensitization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005;82:721–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

