Highly frequent anti-idiotype antibody in cynomolgus monkeys developed against mouse-derived regions of anti-Fas antibody humanized by complementarity determining region grafting
- PMID: 19645714
- PMCID: PMC2757695
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00326.x
Highly frequent anti-idiotype antibody in cynomolgus monkeys developed against mouse-derived regions of anti-Fas antibody humanized by complementarity determining region grafting
Abstract
Background and purpose: We investigated the immunogenicity of a humanized anti-human Fas monoclonal antibody, R-125224, in cynomolgus monkeys to estimate its efficacy, as well as its toxicity in clinical situations.
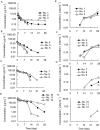
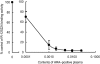
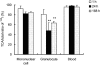
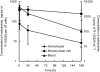
Experimental approach: R-125224 was intravenously administered to cynomolgus monkeys at single doses of 0.4, 1.2, 6 and 30 mg kg(-1), and the plasma concentrations of R-125224 and anti-R-125224 antibody (ARA) were measured. We conducted a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to determine which part of R-125224 was recognized by ARA. We also examined the retention of radioactivity in mononuclear cells and granulocytes after the injection of [(125)I]-R-125224 to a collagen-induced arthritis monkey model.
Key results: After i.v. administration of R-125224, the elimination of the plasma R-125224 concentrations was accelerated at around 10 days post-dose, and 10 of 12 monkeys were ARA positive. From an epitope analysis of ARA, the ARA produced in monkeys recognized the mouse-derived regions located in complementarity determining regions, but could not recognize the human IgG. After the injection of [(125)I]-R-125224 to a collagen-induced arthritis monkey model, a significantly longer retention of the radioactivity in mononuclear cells compared to granulocytes was observed.
Conclusions and implications: In monkeys, the development of antibodies against R-125224 is rapid and highly frequent. Our hypothesis is that this highly frequent development of ARA might be due to the binding of R-125224 to immune cells, and its circulation in monkey blood might contribute to an increase in its chances of being recognized as an immunogen.
Figures
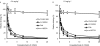
Similar articles
-
Tissue distribution of humanized anti-human Fas monoclonal antibody (R-125224) based on fas antigen-antibody reaction in collagen-induced arthritis monkeys.Life Sci. 2007 May 8;80(22):2005-14. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.02.043. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17477938
-
Immunogenicity screening assay development for a novel human-mouse chimeric anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody (Metuzumab).J Immunol Methods. 2016 Jun;433:38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2016.02.022. Epub 2016 Mar 2. J Immunol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26944771
-
Antibody response against a possible arthritogenic epitope on human type II collagen induced by anti-idiotypic antibody.J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1487-94. J Immunol. 1989. PMID: 2465342
-
The anti-idiotypic response by cynomolgus monkeys to humanized anti-Tac is primarily directed to complementarity-determining regions H1, H2, and L3.J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):3086-90. J Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8454876
-
Correlation of pharmacodynamic activity, pharmacokinetics, and anti-product antibody responses to anti-IL-21R antibody therapeutics following IV administration to cynomolgus monkeys.J Transl Med. 2010 Apr 26;8:41. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-41. J Transl Med. 2010. PMID: 20420683 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Population pharmacokinetics of the humanised monoclonal antibody, HuHMFG1 (AS1402), derived from a phase I study on breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2010 Mar 2;102(5):827-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605560. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20160731 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing production and cytotoxic activity of polymeric soluble FasL-based chimeric proteins by concomitant expression of soluble FasL.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 26;8(8):e73375. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073375. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benincosa LJ, Chow FS, Tobia LP, Kwok DC, Davis CB, Jusko WJ. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a humanized monoclonal antibody to factor IX in cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;292:810–816. - PubMed
-
- Co MS, Landolfe NF, Nagy JO, Tan JH, Vexler V, Vasquez M, et al. Properties and pharmacokinetics of two humanized antibodies specific for l-selectin. Immunotechnology. 1999;4:253–266. - PubMed
-
- Coffey GP, Fox JA, Pippig S, Palmieri S, Reitz B, Gonzales M, et al. Tissue distribution and receptor-mediated clearance of anti-CD11A antibody in mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005;33:623–629. - PubMed
-
- Davis CB, Hepburn TW, Urbanski JJ, Kwok DC, Hart TK, Herzyk DJ, et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetic evaluation of the respiratory syncytial virus-specific reshaped human monoclonal antibody RSHZ19. Drug Metab Dispos. 1995;23(10):1028–1036. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

