Ligands, their receptors and ... plasma membranes
- PMID: 19647036
- PMCID: PMC7116919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.07.022
Ligands, their receptors and ... plasma membranes
Abstract
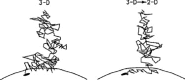
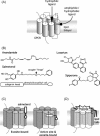
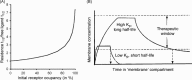
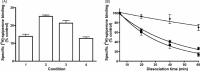
Ligand-receptor interactions are customarily described by equations that apply to solutes. Yet, most receptors are present in cell membranes so that sufficiently lipophilic ligands could reach the receptor by a two-dimensional approach within the membrane. As summarized in this review, this may affect the ligand-receptor interaction in many ways. Biophysicians calculated that, compared to a three-dimensional approach from the liquid phase, such approach could alter the time the ligands need to find a receptor. Biochemists found that ligand incorporation in lipid bilayers modifies their conformation. This, along with the depth at which the ligands reside in the bilayer, will affect the probability of successful receptor interaction. Novel mechanisms were also introduced, including "exosite" binding and ligand translocation between the receptor's alpha-helical transmembrane domains. Pharmacologists focused attention at ligand concentrations in membrane, their adsorption and release rates and the effects thereof on ligand potency and residence time at the receptor.
Figures
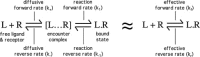

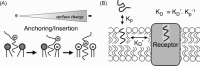
References
-
- Adam G., Delbrück M. Reduction of dimensionality in biological diffusion processes. In: Rich A., Davidson N., Freeman W.H., editors. Structural Chemistry and Molecular Biology. W.H. Freeman & Co.; San Francisco: 1968. pp. 198–215.
-
- Aiello M., Moran O., Pisciotta M., Gambale F. Interaction between dihydropyridines and phospholipid bilayers: a molecular dynamics simulation. Eur. Biophys. J. 1998;27:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Anderson G.P. In: Anderson G.P., Chapman I.D., Morley J., editors. vol. 34. Birkhauser Verlag; 1991. pp. 97–115. (In New Drugs for Asthma Therapy. Agents and Actions Supplement).
-
- Anderson G.P. Formoterol: pharmacology, molecular basis of agonism, and mechanism of long duration of a highly potent and selective β2-adrenoceptor agonist bronchodilator. Life Sci. 1993;52:2145–2160. - PubMed
-
- Anderson G.P., Lindén A., Rabe K.F. Why are long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonists long-acting? Eur. Respir. J. 1994;7:569–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

