The hexosamine signaling pathway: O-GlcNAc cycling in feast or famine
- PMID: 19647043
- PMCID: PMC2815088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.017
The hexosamine signaling pathway: O-GlcNAc cycling in feast or famine
Abstract
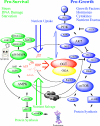
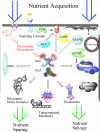
The enzymes of O-GlcNAc cycling couple the nutrient-dependent synthesis of UDP-GlcNAc to O-GlcNAc modification of Ser/Thr residues of key nuclear and cytoplasmic targets. This series of reactions culminating in O-GlcNAcylation of targets has been termed the hexosamine signaling pathway (HSP). The evolutionarily ancient enzymes of O-GlcNAc cycling have co-evolved with other signaling effecter molecules; they are recruited to their targets by many of the same mechanisms used to organize canonic kinase-dependent signaling pathways. This co-recruitment of the enzymes of O-GlcNAc cycling drives a binary switch impacting pathways of anabolism and growth (nutrient uptake) and catabolic pathways (nutrient sparing and salvage). The hexosamine signaling pathway (HSP) has thus emerged as a versatile cellular regulator modulating numerous cellular signaling cascades influencing growth, metabolism, cellular stress, circadian rhythm, and host-pathogen interactions. In mammals, the nutrient-sensing HSP has been harnessed to regulate such cell-specific functions as neutrophil migration, and activation of B-cells and T-cells. This review summarizes the diverse approaches being used to examine O-GlcNAc cycling. It will emphasize the impact O-GlcNAcylation has upon signaling pathways that may be become deregulated in diseases of the immune system, diabetes mellitus, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




References
-
- Love DC, Hanover JA. The hexosamine signaling pathway: deciphering the “O-GlcNAc code”. Sci STKE. 2005;2005:re13. - PubMed
-
- Hart GW, Housley MP, Slawson C. Cycling of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins. Nature. 2007;446:1017–1022. - PubMed
-
- Roos MD, Hanover JA. Structure of O-linked GlcNAc transferase: mediator of glycan-dependent signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;271:275–280. - PubMed
-
- Hanover JA. Glycan-dependent signaling: O-linked N-acetylglucosamine. FASEB J. 2001;15:1865–1876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

