The X-chromosome instability phenotype in Alzheimer's disease: a clinical sign of accelerating aging?
- PMID: 19647374
- PMCID: PMC2787990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.06.046
The X-chromosome instability phenotype in Alzheimer's disease: a clinical sign of accelerating aging?
Abstract
Premature centromere division, or premature centromere separation (PCS), occurs when chromatid separation is dysfunctional, occurring earlier than usual during the interphase stage of mitosis. This phenomenon, seen in Robert's syndrome and various cancers, has also been documented in peripheral as well as neuronal cells of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In the latter instances, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), applied to the centromere region of the X-chromosome in interphase nuclei of lymphocytes from peripheral blood in AD patients, demonstrated premature chromosomal separation before mitotic metaphase directly after completion of DNA replication in G(2) phase of the cell cycle. Furthermore, and perhaps unexpectedly given the presumptive post-mitotic status of terminally differentiated neurons, neurons in AD patients also showed significantly increased levels of PCS of the X-chromosome. Taken together with other phenomena such as cell cycle re-activation and ectopic re-expression of cyclins and cyclin dependent proteins, we propose that AD is an oncogenic phenotype leading to accelerated aging of the affected brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The sources of funding have no role in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures
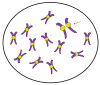
References
-
- Nasmyth K. Segregating sister genomes: the molecular biology of chromosome separation. Science. 2002;297:559–565. - PubMed
-
- Vig BK, Paweletz N. Centromere separation: emerging relationship with aneuploidy. In: Kappas A, editor. Mechanisms of Environmental Mutagenesis-Carcinogenesis. Plenum Press; New York: 1990.
-
- Fitzgerald PH, Archer SA, Morris CM. Evidence for the repeated primary non-disjunction of chromosome 21 as a result of premature centromere division (PCD) Hum Genet. 1986;72:58–62. - PubMed
-
- Migliore L, Botto N, Scarpato R, Petrozzi L, Cipriani G, Bonuccelli U. Preferential occurrence of chromosome 21 malsegregation in peripheral blood lymphocytes of Alzheimer disease patients. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1999;87:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Migliore L, Testa A, Scarpato R, Pavese N, Petrozzi L, Bonuccelli U. Spontaneous and induced aneuploidy in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Hum Genet. 1997;101:299–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

