A quorum-sensing antagonist targets both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors and controls bacterial pathogenicity
- PMID: 19647512
- PMCID: PMC2741501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.05.029
A quorum-sensing antagonist targets both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors and controls bacterial pathogenicity
Abstract
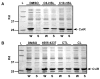
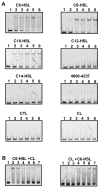
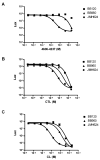
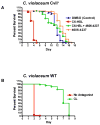
Quorum sensing is a process of bacterial communication involving production and detection of secreted molecules called autoinducers. Gram-negative bacteria use acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) autoinducers, which are detected by one of two receptor types. First, cytoplasmic LuxR-type receptors bind accumulated intracellular AHLs. AHL-LuxR complexes bind DNA and alter gene expression. Second, membrane-bound LuxN-type receptors bind accumulated extracellular AHLs. AHL-LuxN complexes relay information internally by phosphorylation cascades that direct gene expression changes. Here, we show that a small molecule, previously identified as an antagonist of LuxN-type receptors, is also a potent antagonist of the LuxR family, despite differences in receptor structure, localization, AHL specificity, and signaling mechanism. Derivatives were synthesized and optimized for potency, and in each case, we characterized the mode of action of antagonism. The most potent antagonist protects Caenorhabditis elegans from quorum-sensing-mediated killing by Chromobacterium violaceum, validating the notion that targeting quorum sensing has potential for antimicrobial drug development.
Figures
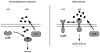
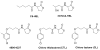

References
-
- Aballay A, Ausubel FM. Caenorhabditis elegans as a host for the study of host-pathogen interactions. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002;5:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Bassler BL, Wright M, Showalter RE, Silverman MR. Intercellular signalling in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes regulating expression of luminescence. Mol Microbiol. 1993;9:773–786. - PubMed
-
- Bassler BL, Wright M, Silverman MR. Multiple signalling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13:273–286. - PubMed
-
- Cao JG, Meighen EA. Purification and structural identification of an autoinducer for the luminescence system of Vibrio harveyi. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:21670–21676. - PubMed
-
- Dhakal BK, Lee W, Kim YR, Choy HE, Ahnn J, Rhee JH. Caenorhabditis elegans as a simple model host for Vibrio vulnificus infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;346:751–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

