Improving global and regional resolution of male lineage differentiation by simple single-copy Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat polymorphisms
- PMID: 19647704
- PMCID: PMC3312386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2009.01.009
Improving global and regional resolution of male lineage differentiation by simple single-copy Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat polymorphisms
Abstract
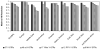
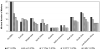
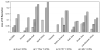
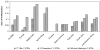
We analyzed 67 short tandem repeat polymorphisms from the non-recombining part of the Y-chromosome (Y-STRs), including 49 rarely studied simple single-copy (ss)Y-STRs and 18 widely used Y-STRs, in 590 males from 51 populations belonging to 8 worldwide regions (HGDP-CEPH panel). Although autosomal DNA profiling provided no evidence for close relationship, we found 18 Y-STR haplotypes (defined by 67 Y-STRs) that were shared by two to five men in 13 worldwide populations, revealing high and widespread levels of cryptic male relatedness. Maximal (95.9%) haplotype resolution was achieved with the best 25 out of 67 Y-STRs in the global dataset, and with the best 3-16 markers in regional datasets (89.6-100% resolution). From the 49 rarely studied ssY-STRs, the 25 most informative markers were sufficient to reach the highest possible male lineage differentiation in the global (92.2% resolution), and 3-15 markers in the regional datasets (85.4-100%). Considerably lower haplotype resolutions were obtained with the three commonly used Y-STR sets (Minimal Haplotype, PowerPlex Y, and AmpFlSTR Yfiler. Six ssY-STRs (DYS481, DYS533, DYS549, DYS570, DYS576 and DYS643) were most informative to supplement the existing Y-STR kits for increasing haplotype resolution, or - together with additional ssY-STRs - as a new set for maximizing male lineage differentiation. Mutation rates of the 49 ssY-STRs were estimated from 403 meiotic transfers in deep-rooted pedigrees, and ranged from approximately 4.8 x 10(-4) for 31 ssY-STRs with no mutations observed to 1.3 x 10(-2) and 1.5 x 10(-2) for DYS570 and DYS576, respectively, the latter representing the highest mutation rates reported for human Y-STRs so far. Our findings thus demonstrate that ssY-STRs are useful for maximizing global and regional resolution of male lineages, either as a new set, or when added to commonly used Y-STR sets, and support their application to forensic, genealogical and anthropological studies.
Figures
References
-
- Kayser M, Caglia A, Corach D, Fretwell N, Gehrig C, Graziosi G, Heidorn F, Herrmann S, Herzog B, Hidding M, Honda K, Jobling M, Krawczak M, Leim K, Meuser S, Meyer E, Oesterreich W, Pandya A, Parson W, Penacino G, Perez-Lezaun A, Piccinini A, Prinz M, Schmitt C, Roewer L, et al. Evaluation of Y-chromosomal STRs: a multicenter study. Int J Legal Med. 1997;110:125–133. 141–129. - PubMed
-
- Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C. The human Y chromosome: an evolutionary marker comes of age. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:598–612. - PubMed
-
- Kayser M, Vermeulen M, Knoblauch H, Schuster H, Krawczak M, Roewer L. Relating two deep-rooted pedigrees from Central Germany by high-resolution Y-STR haplotyping. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2007;1:125–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

