PACAP-cytokine interactions govern adrenal neuropeptide biosynthesis after systemic administration of LPS
- PMID: 19647754
- PMCID: PMC2783598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.07.034
PACAP-cytokine interactions govern adrenal neuropeptide biosynthesis after systemic administration of LPS
Erratum in
- Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jun;58(7):1187
Abstract
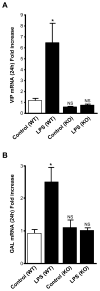
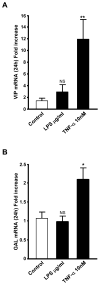
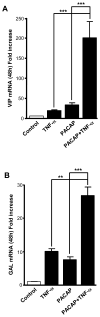
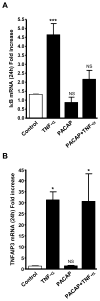
We have examined induction of neuropeptide expression in adrenal medulla after treatment of mice with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a model for septic shock, which activates both immune and stress responses in vivo. Messenger RNAs encoding vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) and galanin, both modulators of steroidogenesis in neighboring adrenal cortex, are up-regulated at 24 h (eight-fold for VIP and two-fold for galanin) after LPS injection, and remain elevated for the following 24 h. Up-regulation of VIP and galanin by LPS is abrogated in pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)-deficient mice, suggesting an interaction between LPS, or LPS-induced cytokines, and PACAP released in adrenal medulla from the splanchnic nerve. Treatment of cultured chromaffin cells with 100 nM PACAP and 10 nM tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), a cytokine whose production is elevated by LPS, results in long-term synergistic up-regulation of VIP and galanin mRNA. PACAP blocks the earlier induction by TNF-alpha of mRNA encoding inhibitor of NF-kappaB alpha (I kappaB alpha), normally a negative autoregulator of TNF-alpha signaling through nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), without affecting the induction of TNF-alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3), another NF-kappaB-dependent gene induced by TNF-alpha in chromaffin cells. By acting downstream of NF-kappaB to inhibit I kappaB alpha gene induction by TNF-alpha, PACAP may block I kappaB alpha-dependent negative autoregulation of TNF-alpha signaling through NF-kappaB, prolonging TNF-alpha-dependent signaling to neuropeptide-encoding genes in chromaffin cells. This mechanism may also underlie PACAP-dependent neuropeptide gene induction by LPS in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Ait-Ali D, Turquier V, Grumolato L, Yon L, Jourdain M, Alexandre D, Eiden LE, Vaudry H, Anouar Y. The proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 stimulate neuropeptide gene transcription and secretion in adrenochromaffin cells via activation of extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 protein kinases, and activator protein-1 transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18:1721–1739. - PubMed
-
- Ait-Ali D, Turquier V, Tanguy Y, Thouennon E, Ghzili H, Mounien L, Derambure C, Jegou S, Salier JP, Vaudry H, Eiden LE, Anouar Y. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha persistently activates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling through the type 2 TNF receptor in chromaffin cells: implications for long-term regulation of neuropeptide gene expression in inflammation. Endocrinology. 2008;149:2840–2852. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreis PG, Tortorella C, Ziolkowska A, Spinazzi R, Malendowicz LK, Neri G, Nussdorfer GG. Evidence for a paracrine role of endogenous adrenomedullary galanin in the regulation of glucocorticoid secretion in the rat adrenal gland. Int J Mol Med. 2007;19:511–515. - PubMed
-
- Anouar Y, MacArthur L, Cohen J, Iacangelo AL, Eiden LE. Identification of a TPA-responsive element mediating preferential transactivation of the galanin gene promoter in chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:6823–6831. - PubMed
-
- Arranz A, Androulidaki A, Zacharioudaki V, Martinez C, Margioris AN, Gomariz RP, Tsatsanis C. Vasoactive intestinal peptide suppresses toll-like receptor 4 expression in macrophages via Akt1 reducing their responsiveness to lipopolysaccharide. Mol Immunol. 2008;45:2970–2980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

