Focused ultrasound effects on nerve action potential in vitro
- PMID: 19647923
- PMCID: PMC2752482
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2009.05.002
Focused ultrasound effects on nerve action potential in vitro
Abstract
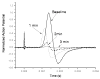
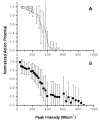
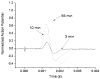
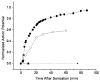
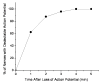
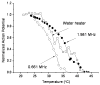
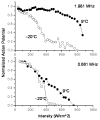
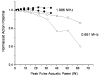
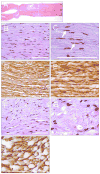
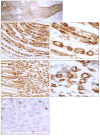
Minimally invasive applications of thermal and mechanical energy to selective areas of the human anatomy have led to significant advances in treatment of and recovery from typical surgical interventions. Image-guided focused ultrasound allows energy to be deposited deep into the tissue, completely noninvasively. There has long been interest in using this focal energy delivery to block nerve conduction for pain control and local anesthesia. In this study, we have performed an in vitro study to further extend our knowledge of this potential clinical application. The sciatic nerves from the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) were subjected to focused ultrasound (at frequencies of 0.661 MHz and 1.986 MHz) and to heated Ringer's solution. The nerve action potential was shown to decrease in the experiments and correlated with temperature elevation measured in the nerve. The action potential recovered either completely, partially or not at all, depending on the parameters of the ultrasound exposure. The reduction of the baseline nerve temperature by circulating cooling fluid through the sonication chamber did not prevent the collapse of the nerve action potential; but higher power was required to induce the same endpoint as without cooling. These results indicate that a thermal mechanism of focused ultrasound can be used to block nerve conduction, either temporarily or permanently.
Figures
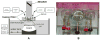
Similar articles
-
Nerve conduction block in diabetic rats using high-intensity focused ultrasound for analgesic applications.Br J Anaesth. 2015 May;114(5):840-6. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu443. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Br J Anaesth. 2015. PMID: 25904608
-
In vitro effects of ultrasound with different energies on the conduction properties of neural tissue.Ultrasonics. 2005 Jun;43(7):560-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2004.12.003. Epub 2004 Dec 18. Ultrasonics. 2005. PMID: 15950031
-
Irreversible conduction block in isolated nerve by high concentrations of local anesthetics.Anesthesiology. 1994 May;80(5):1082-93. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199405000-00017. Anesthesiology. 1994. PMID: 8017646
-
[Ultrasound-guided sciatic nerve block].Masui. 2008 May;57(5):580-7. Masui. 2008. PMID: 18516885 Review. Japanese.
-
Use of ultrasound in drug delivery systems: emphasis on experimental methodology and mechanisms.Int J Hyperthermia. 2012;28(4):282-9. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2012.668640. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012. PMID: 22621730 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the bioeffects of low-intensity focused ultrasound and the benefits of a cellular approach.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1047324. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1047324. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36439246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Image-guided ultrasound phased arrays are a disruptive technology for non-invasive therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2016 Sep 7;61(17):R206-48. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/61/17/R206. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Phys Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27494561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sonomechanobiology: Vibrational stimulation of cells and its therapeutic implications.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023 Apr 21;4(2):021301. doi: 10.1063/5.0127122. eCollection 2023 Jun. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023. PMID: 38504927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenic Flare Response following Image-Guided Focused Ultrasound in the Mouse Peripheral Nervous System in Vivo.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021 Sep;47(9):2759-2767. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2021.04.030. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34176702 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral focused ultrasound stimulation and its applications: From therapeutics to human-computer interaction.Front Neurosci. 2023 Apr 14;17:1115946. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1115946. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37123351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adrianov OS, Vykhodtseva N, Fokin VF, Avirom VM. Method of local action by focused ultrasound on deep brain structures in unrestrained unanesthetized animals. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1984a;98:115–117. - PubMed
-
- Adrianov OS, Vykhodtseva N, Fokin VF, Uranova N, Avirom VM. Reversible functional shutdown of the optic tract on exposure to focused ultrasound. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1984b;97:760–762. - PubMed
-
- Adrianov OS, Vykhodtseva NI, Fokin VF, Avirom VM. [Method of local action by focussed ultrasound on deep brain structures in unrestrained unanesthetized animals] Metod lokal’nogo vozdeistviia fokusirovannym ul’trazvukom na gluboko raspolozhennye struktury mozga neobezdvizhennogo nenarkotizirovannogo zhivotnogo. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1984c;98:115–117. - PubMed
-
- Adrianov OS, Vykhodtseva NI, Gavrilov LR. [Use of focused ultrasound for local effects on deep brain structures] Primenenie fokusirovannogo ul’trazvuka dlia lokal’nogo vozdeistviia na glubokie struktury mozga. Fiziol Zh SSSR. 1984d;70:1157–1166. - PubMed
-
- Bachtold MR, Rinaldi PC, Jones JP, Reines F, Price LR. Focused ultrasound modifications of neural circuit activity in a mammalian brain. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1998;24:557–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

