Efficacy and safety of nebivolol in elderly heart failure patients with impaired renal function: insights from the SENIORS trial
- PMID: 19648605
- PMCID: PMC2729679
- DOI: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfp104
Efficacy and safety of nebivolol in elderly heart failure patients with impaired renal function: insights from the SENIORS trial
Abstract
Aim: To determine the safety and efficacy of nebivolol in elderly heart failure (HF) patients with renal dysfunction.
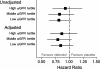
Methods and results: SENIORS recruited patients aged 70 years or older with symptomatic HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, and randomized them to nebivolol or placebo. Patients (n = 2112) were divided by tertile of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Mean age of patients was 76.1 years, 35% of patients had an ejection fraction of >35%, and 37% were women resulting in a unique cohort, far more representative of clinical practice than previous trials. eGFR was strongly associated with outcomes and nebivolol was similarly efficacious across eGFR tertiles. The primary outcome rate (all-cause mortality or cardiovascular hospital admission) and adjusted hazard ratio for nebivolol use in those with low eGFR was 40% and 0.84 (95% CI 0.67-1.07), 31% and 0.79 (0.60-1.04) in the middle tertile, and 29% and 0.86 (0.65-1.14) in the highest eGFR tertile. There was no interaction noted between renal function and the treatment effect (P = 0.442). Nebivolol use in patients with moderate renal impairment (eGFR <60) was not associated with major safety concerns, apart from higher rates of drug-discontinuation due to bradycardia.
Conclusion: Nebivolol is safe and has a similar effect in elderly HF patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Ahmad A, Rand WM, Manjunath G, Konstam MA, Salem DN, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ. Reduced kidney function and anemia as risk factors for mortality in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38:955–962. - PubMed
-
- Huynh BC, Rovner A, Rich MW. Long-term survival in elderly patients hospitalized for heart failure: 14-year follow-up from a prospective randomized trial. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1892–1898. - PubMed
-
- Velavan P, Khan NK, Goode K, Rigby AS, Loh PH, Komajda M, Follath F, Swedberg K, Madeira H, Cleland JG. Predictors of short term mortality in heart failure - Insights from the Euro Heart Failure survey. Int J Cardiol. 2008 doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.08.004. [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Rich MW. Office management of heart failure in the elderly. Am J Med. 2005;118:342–348. - PubMed
-
- Saltzman HE, Sharma K, Mather PJ, Rubin S, Adams S, Whellan DJ. Renal dysfunction in heart failure patients: what is the evidence? Heart Fail Rev. 2007;12:37–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

