A genome-wide association study identifies a new ovarian cancer susceptibility locus on 9p22.2
- PMID: 19648919
- PMCID: PMC2844110
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.424
A genome-wide association study identifies a new ovarian cancer susceptibility locus on 9p22.2
Abstract
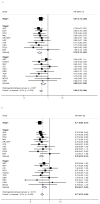
Epithelial ovarian cancer has a major heritable component, but the known susceptibility genes explain less than half the excess familial risk. We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify common ovarian cancer susceptibility alleles. We evaluated 507,094 SNPs genotyped in 1,817 cases and 2,353 controls from the UK and approximately 2 million imputed SNPs. We genotyped the 22,790 top ranked SNPs in 4,274 cases and 4,809 controls of European ancestry from Europe, USA and Australia. We identified 12 SNPs at 9p22 associated with disease risk (P < 10(-8)). The most significant SNP (rs3814113; P = 2.5 x 10(-17)) was genotyped in a further 2,670 ovarian cancer cases and 4,668 controls, confirming its association (combined data odds ratio (OR) = 0.82, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.79-0.86, P(trend) = 5.1 x 10(-19)). The association differs by histological subtype, being strongest for serous ovarian cancers (OR 0.77, 95% CI 0.73-0.81, P(trend) = 4.1 x 10(-21)).
Figures

References
-
- Pharoah PD, Ponder BA. The genetics of ovarian cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2002;16:449–468. - PubMed
-
- Stratton JF, Pharoah P, Smith SK, Easton D, Ponder BA. A systematic review and meta-analysis of family history and risk of ovarian cancer. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998;105:493–499. - PubMed
-
- Antoniou AC, Easton DF. Risk prediction models for familial breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2006;2:257–274. - PubMed
-
- Pharoah PD, Antoniou AC, Easton DF, Ponder BA. Polygenes, risk prediction, and targeted prevention of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2796–2803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA71766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA61107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- A10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA058860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-58860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA016056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-35137/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA87538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11022/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A8339/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA058860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA092044/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 19275/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA105009/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035137/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-55424/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11021/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0801875/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA054419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA-122443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-92044/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- A6187/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01-CA- 58598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA112523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA136393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- A10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA114343/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- N01 PC035137/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA114343/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

