Plasma Coenzyme Q10 Predicts Lipid-lowering Response to High-Dose Atorvastatin
- PMID: 19649137
- PMCID: PMC2598393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2008.05.001
Plasma Coenzyme Q10 Predicts Lipid-lowering Response to High-Dose Atorvastatin
Abstract
Background: Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a provitamin synthesized via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, and thus may serve as a potential marker of intrinsic HMG-CoA reductase activity. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) decrease CoQ10, although it is unclear whether this is due to reductions in lipoproteins, which transport CoQ10.
Objectives: We evaluated whether baseline plasma CoQ10 concentrations predict the lipid-lowering response to high-dose atorvastatin, and to what extent CoQ10 changes following atorvastatin therapy depend on lipoprotein changes.
Methods: Individuals without dyslipidemia or known cardiovascular disease (n=84) received atorvastatin 80 mg daily for 16 weeks. Blood samples collected at baseline and after 4, 8, and 16 weeks of treatment were assayed for CoQ10.
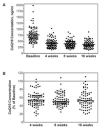
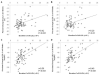
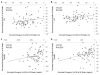
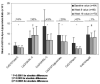
Results: Individuals with higher baseline CoQ10:LDL-C ratios displayed diminished absolute and percent LDL-C reductions at 8 and 16 weeks of atorvastatin treatment (P<0.001 to 0.01). After 16 weeks of atorvastatin, plasma CoQ10 decreased 45% from 762+/-301 ng/ml to 374+/-150 ng/ml (P<0.001). CoQ10 changes were correlated with LDL-C and apolipoprotein B changes (r=0.27-0.38, P=0.001-0.02), but remained significant when normalized to all lipoproteins. CoQ10 changes were not associated with adverse drug reactions.
Conclusion: Baseline CoQ10:LDL-C ratio was associated with the degree of LDL-C response to atorvastatin. Atorvastatin decreased CoQ10 concentrations in a manner that was not completely dependent on lipoprotein changes. The utility of CoQ10 as a predictor of atorvastatin response should be further explored in patients with dyslipidemia.
Keywords: Coenzyme Q10; HMG CoA-reductase inhibitors; biomarkers; lipids; pharmacology.
Figures
References
-
- Zineh I, Welder GJ, DeBella AE, Arant CB, Wessel TR, Schofield RS. Atorvastatin effect on circulating and leukocyte-produced CD40 ligand concentrations in people with normal cholesterol levels: a pilot study. Pharmacotherapy. 2006;26:1572–7. - PubMed
-
- Pedro-Botet J, Schaefer EJ, Bakker-Arkema RG, Black DM, Stein EM, Corella D, Ordovas JM. Apolipoprotein E genotype affects plasma lipid response to atorvastatin in a gender specific manner. Atherosclerosis. 2001;158:183–93. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Braunwald E, McCabe CH, Rader DJ, Rouleau JL, Belder R, Joyal SV, Hill KA, Pfeffer MA, Skene AM. Intensive versus moderate lipid lowering with statins after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1495–504. - PubMed
-
- LaRosa JC, Grundy SM, Waters DD, Shear C, Barter P, Fruchart JC, Gotto AM, Greten H, Kastelein JJ, Shepherd J, Wenger NK. Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1425–35. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
