Classification of cardiac patient states using artificial neural networks
- PMID: 19649222
- PMCID: PMC2719156
Classification of cardiac patient states using artificial neural networks
Abstract
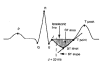
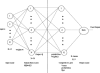
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a nonstationary signal; therefore, the disease indicators may occur at random in the time scale. This may require the patient be kept under observation for long intervals in the intensive care unit of hospitals for accurate diagnosis. The present study examined the classification of the states of patients with certain diseases in the intensive care unit using their ECG and an Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) classification system. The states were classified into normal, abnormal and life threatening. Seven significant features extracted from the ECG were fed as input parameters to the ANN for classification. Three neural network techniques, namely, back propagation, self-organizing maps and radial basis functions, were used for classification of the patient states. The ANN classifier in this case was observed to be correct in approximately 99% of the test cases. This result was further improved by taking 13 features of the ECG as input for the ANN classifier.
Keywords: Electrocardiogram; Heart rate; Intensive care unit; Neural network; Radial basis function; Self-organizing map.
Figures



References
-
- Li G, Ye W, Lin L, Yu Q, Yu X. An artificial intelligence approach to ECG analysis. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2000;19:95–100. - PubMed
-
- Silipo R, Marchesi C. Artificial neural networks for automatic ECG analysis. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 1998;46:1417–25.
-
- van Gils M, Jansen H, Nieminen K, Summers R, Weller PR. Using artificial neural network for classifying ICU patient states. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1997;16:41–7. - PubMed
-
- Williams JL, Lesaffre E. Comparison of multigroup logistic and linear discriminant ECG and VCG classification. J Electrocardiol. 1987;20:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Coast AD, Stern RM, Casio GG, Britter SA. An approach to cardiac arrhythmia analysis using hidden Markov models. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1990;37:826–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
