Catecholamine-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats is associated with the activation of p70 kinase and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 2
- PMID: 19649237
- PMCID: PMC2719175
Catecholamine-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats is associated with the activation of p70 kinase and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 2
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of intravenous infusion of adrenergic, hypertrophic agonists on the activity of the ribosomal S6 (p70(S6)) kinase and the c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 2 (JNK2) in adult rat hearts.
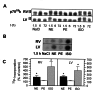
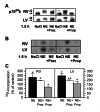
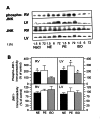
Animals and methods: Noradrenaline (NA), isoproterenol (ISO), phenylephrine (PE), NA in combination with propranolol (NA+Prop) and NA in combination with prazosin (NA+Praz) were continuously intravenously infused in rat hearts for up to 72 h. The expression and phosphorylation status of JNK2 and p70(S6) kinase were investigated by western blotting and use of specific and phosphospecific antibodies. The activity of p70(S6) kinase was measured by incorporation of (32)P-labelled phosphate into the specific substrate S6 peptide.
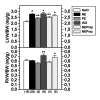
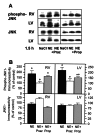
Results: The ratio of left ventricular weight to body weight was increased by NA, and by alpha- (PE, NA+Prop) and beta-adrenergic (ISO, NA+Praz) stimulation. Right ventricular weight to body weight ratio was higher only after beta-adrenergic stimulation (ISO, NA+Praz). p70(S6) kinase activity was stimulated predominantly through beta-adrenoceptors in parallel with left and right ventricular hypertrophy. Activation of JNK2 was mainly dependent on alpha-adrenoceptor activation, which led to hypertrophy of only the left ventricle.
Conclusions: The activation of p70(S6) kinase and JNK2 may be implicated in the development of catecholamine-induced cardiac hypertrophy in vivo.
Keywords: Catecholamines; Hypertrophy; Rat; Ribosomal S6 kinase; c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of p70(S6) kinase by beta-adrenoceptor agonists on adult cardiomyocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998 Oct;30(10):2059-67. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1998.0768. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9799659
-
Rapamycin inhibits alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-stimulated cardiac myocyte hypertrophy but not activation of hypertrophy-associated genes. Evidence for involvement of p70 S6 kinase.Circ Res. 1997 Aug;81(2):176-86. doi: 10.1161/01.res.81.2.176. Circ Res. 1997. PMID: 9242178
-
Comitogenic effect of catecholamines on rat cardiac fibroblasts in culture.Cardiovasc Res. 2000 Nov;48(2):274-84. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00170-x. Cardiovasc Res. 2000. PMID: 11054474
-
Catecholamine-induced cardiac hypertrophy: significance of proto-oncogene expression.J Mol Med (Berl). 1997 Nov-Dec;75(11-12):849-59. doi: 10.1007/s001090050176. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997. PMID: 9428617 Review.
-
Regulation of phospholamban and troponin-I phosphorylation in the intact rat cardiomyocytes by adrenergic and cholinergic stimuli: roles of cyclic nucleotides, calcium, protein kinases and phosphatases and depolarization.Mol Cell Biochem. 1995 Aug-Sep;149-150:103-26. doi: 10.1007/BF01076569. Mol Cell Biochem. 1995. PMID: 8569720 Review.
References
-
- Irlbeck M, Mühling O, Iwai T, Zimmer HG. Different response of the rat left and right heart to norepinephrine. Cardiovasc Res. 1996;31:157–62. - PubMed
-
- Barth W, Deten A, Bauer M, Reinohs M, Leicht M, Zimmer HG. Differential remodeling of the left and right heart after norepinephrine treatment in rats: studies on cytokines and collagen. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2000;32:273–84. - PubMed
-
- Zierhut W, Zimmer HG. Significance of myocardial alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in catecholamine-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 1989;65:1417–25. - PubMed
-
- Lee HR, Henderson SA, Reynolds R, Dunnmon P, Yuan D, Chien KR. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Effects on myosin light chain-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:7352–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
