Activation of NF-kB pathway by virus infection requires Rb expression
- PMID: 19649275
- PMCID: PMC2713421
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006422
Activation of NF-kB pathway by virus infection requires Rb expression
Abstract
The retinoblastoma protein Rb is a tumor suppressor involved in cell cycle control, differentiation, and inhibition of oncogenic transformation. Besides these roles, additional functions in the control of immune response have been suggested. In the present study we investigated the consequences of loss of Rb in viral infection. Here we show that virus replication is increased by the absence of Rb, and that Rb is required for the activation of the NF-kB pathway in response to virus infection. These results reveal a novel role for tumor suppressor Rb in viral infection surveillance and further extend the concept of a link between tumor suppressors and antiviral activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
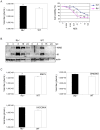
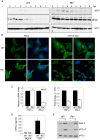
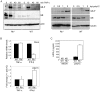
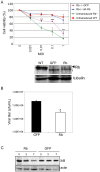
Similar articles
-
The RB tumor suppressor at the intersection of proliferation and immunity: relevance to disease immune evasion and immunotherapy.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(24):3812-9. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1010922. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25714546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor promotes efficient human cytomegalovirus lytic replication.J Virol. 2015 May;89(9):5012-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00175-15. Epub 2015 Feb 18. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25694602 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Rb phosphorylation leads to H2S-mediated inhibition of NF-kB in acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury in mice.Pancreatology. 2020 Jun;20(4):647-658. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.04.011. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Pancreatology. 2020. PMID: 32402695
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Can Procure Deoxyribonucleotides for Viral DNA Replication in the Absence of Retinoblastoma Protein Phosphorylation.J Virol. 2016 Sep 12;90(19):8634-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00731-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27440891 Free PMC article.
-
The RB protein family in retinal development and retinoblastoma: new insights from new mouse models.Dev Neurosci. 2004;26(5-6):417-34. doi: 10.1159/000082284. Dev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15855771 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of NF-κB activity by the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nonstructural protein 1 for innate immune evasion.Virology. 2017 Oct;510:111-126. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.07.009. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Virology. 2017. PMID: 28715653 Free PMC article.
-
The triumvirate of NF-κB, inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):108255. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108255. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34688149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages, inflammation, and tumor suppressors: ARF, a new player in the game.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:568783. doi: 10.1155/2012/568783. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 23316105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein inhibits NF-κB activation in mouse L929 cells.Virology. 2016 Dec;499:99-104. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27643886 Free PMC article.
-
The RB tumor suppressor at the intersection of proliferation and immunity: relevance to disease immune evasion and immunotherapy.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(24):3812-9. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1010922. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25714546 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Classon M, Harlow E. The retinoblastoma tumour suppressor in development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:910–917. - PubMed
-
- Lu Y, Ussery GD, Muncaster MM, Gallie BL, Blanck G. Evidence for retinoblastoma protein (RB) dependent and independent IFN-gamma responses: RB coordinately rescues IFN-gamma induction of MHC class II gene transcription in noninducible breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 1994;9:1015–1019. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Pattenden S, Bremner R. pRB is required for interferon-gamma-induction of the MHC class II abeta gene. Oncogene. 1999;18:4940–4947. - PubMed
-
- Eason DD, Coppola D, Livingston S, Shepherd AT, Blanck G. Loss of MHC class II inducibility in hyperplastic tissue in Rb-defective mice. Cancer Lett. 2001;171:209–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

