Low circulating maternal adiponectin in patients with pyelonephritis: adiponectin at the crossroads of pregnancy and infection
- PMID: 19650757
- PMCID: PMC2802659
- DOI: 10.1515/jpm.2009.134
Low circulating maternal adiponectin in patients with pyelonephritis: adiponectin at the crossroads of pregnancy and infection
Abstract
Objective: An emerging theme in modern biology is that adipose tissue can respond to metabolic stress, and to inflammatory stimuli, by regulating the secretion of a complex network of soluble mediators, termed adipokines. Adiponectin, the most prevalent circulating adipokine in human, has profound insulin-sensitizing and anti-inflammatory properties. Indeed, the notion that adiponectin plays an important role in the interactions between the metabolic and the immune systems has been strongly suggested. Thus, the aim of this study was to determine if pyelonephritis during pregnancy is associated with changes in maternal serum adiponectin concentrations.
Study design: This cross-sectional study included women in the following groups: 1) normal pregnant women (n=200); and 2) pregnant women with pyelonephritis (n=50). Maternal plasma adiponectin concentrations were determined by ELISA. Non-parametric statistics were used for analyses.
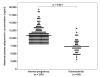
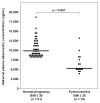
Results: 1) The median maternal plasma adiponectin concentration was lower in patients with pyelonephritis than in those with a normal pregnancy (P<0.001); 2) among pregnant women with a normal weight, patients with pyelonephritis had a lower median plasma adiponectin concentration than those with a normal pregnancy (P<0.001); 3) similarly, among overweight/obese patients, those with pyelonephritis had a lower median plasma adiponectin concentration than those with a normal pregnancy (P<0.001); and 4) the presence of pyelonephritis was independently associated with maternal plasma adiponectin concentrations after adjustment for maternal age, smoking, gestational age at sampling, and pregestational body mass index (BMI).
Conclusion: 1) The findings that acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy is characterized by low maternal plasma concentrations of adiponectin in both lean and overweight/obese patients are novel and concur with the antiinflammatory properties of adiponectin; and 2) the results of this study support the notion that adiponectin may play a role in the intricate interface between inflammation and metabolism during pregnancy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maternal plasma retinol binding protein 4 in acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy.J Perinat Med. 2010 Jul;38(4):359-66. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2010.066. J Perinat Med. 2010. PMID: 20163326 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal plasma concentration of the pro-inflammatory adipokine pre-B-cell-enhancing factor (PBEF)/visfatin is elevated in pregnant patients with acute pyelonephritis.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010 Mar 1;63(3):252-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2009.00804.x. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20085562 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal serum adiponectin multimers in preeclampsia.J Perinat Med. 2009;37(4):349-63. doi: 10.1515/JPM.2009.085. J Perinat Med. 2009. PMID: 19348608 Free PMC article.
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
-
Adipokines underlie the early origins of obesity and associated metabolic comorbidities in the offspring of women with pregestational obesity.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Feb 1;1866(2):165558. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165558. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 31654701 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal plasma retinol binding protein 4 in acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy.J Perinat Med. 2010 Jul;38(4):359-66. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2010.066. J Perinat Med. 2010. PMID: 20163326 Free PMC article.
-
Retinol-binding protein 4: a novel adipokine implicated in the genesis of LGA in the absence of gestational diabetes mellitus.J Perinat Med. 2010 Mar;38(2):147-55. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2010.044. J Perinat Med. 2010. PMID: 20146659 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for differential regulation of the adipokine visfatin in the maternal and fetal compartments in normal spontaneous labor at term.J Perinat Med. 2010 May;38(3):281-8. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2010.045. J Perinat Med. 2010. PMID: 20146661 Free PMC article.
-
Could alterations in maternal plasma visfatin concentration participate in the phenotype definition of preeclampsia and SGA?J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Aug;23(8):857-68. doi: 10.3109/14767050903301017. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010. PMID: 19900033 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue transcriptome in pregnant women with and without spontaneous labor at term: implication of alternative splicing in the metabolic adaptations of adipose tissue to parturition.J Perinat Med. 2016 Oct 1;44(7):813-835. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2015-0259. J Perinat Med. 2016. PMID: 26994472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ Tech.Rep.Ser. 2003;916:i–149. backcover. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi F, Chu JW, Lamendola C, McLaughlin T, Hayden J, Reaven GM, et al. Discrimination between obesity and insulin resistance in the relationship with adiponectin. Diabetes. 2004;53:585–590. - PubMed
-
- Amstey MS. Frequency of adult respiratory distress syndrome in pregnant women who have pyelonephritis. Clin.Infect.Dis. 1992;14:1260–1261. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PD, Mehta NN, Wolfe ML, Hinkle CC, Pruscino L, Comiskey LL, et al. Innate immunity modulates adipokines in humans. J Clin.Endocrinol.Metab. 2007;92:2272–2279. - PubMed
-
- Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun. 1999;257:79–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
