mec-15 encodes an F-box protein required for touch receptor neuron mechanosensation, synapse formation and development
- PMID: 19652181
- PMCID: PMC2766320
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.105726
mec-15 encodes an F-box protein required for touch receptor neuron mechanosensation, synapse formation and development
Abstract
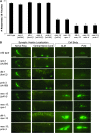
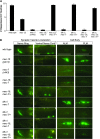
Selective protein degradation is a key regulator of neuronal development and synaptogenesis. Complexes that target proteins for degradation often contain F-box proteins. Here we characterize MEC-15, an F-box protein with WD repeats, which is required for the development and function of Caenorhabditis elegans touch receptor neurons (TRNs). Mutations in mec-15 produce defects in TRN touch sensitivity, chemical synapse formation, and cell-body morphology. All mec-15 mutant phenotypes are enhanced by mutations in a MAP kinase pathway composed of the MAPKKK DLK-1, the MAPKK MKK-4, and the p38 MAPK PMK-3. A mutation of the rpm-1 gene, which encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase that negatively regulates this pathway to promote synaptogenesis, suppresses only the mec-15 cell-body defect. Thus, MEC-15 acts in parallel with RPM-1, implicating a second protein degradation pathway in TRN development. In addition, all mec-15 phenotypes can be dominantly suppressed by mutations in mec-7, which encodes a beta-tubulin, and dominantly enhanced by mutations in mec-12, which encodes an alpha-tubulin. Since mec-15 phenotypes depend on the relative levels of these tubulins, MEC-15 may target proteins whose function is affected by these levels.
Figures




References
-
- Bounoutas, A., and M. Chalfie, 2007. Touch sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Pflugers Arch. 454 691–702. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie, M., and M. Au, 1989. Genetic control of differentiation of the Caenorhabditis elegans touch receptor neurons. Science 243 1027–1033. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie, M., and J. Sulston, 1981. Developmental genetics of the mechanosensory neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 82 358–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

