Pneumoviruses infect eosinophils and elicit MyD88-dependent release of chemoattractant cytokines and interleukin-6
- PMID: 19652202
- PMCID: PMC2756124
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-199497
Pneumoviruses infect eosinophils and elicit MyD88-dependent release of chemoattractant cytokines and interleukin-6
Abstract
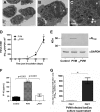
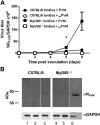
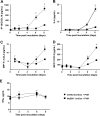
Eosinophils are recruited to the lung in response to infection with pneumovirus pathogens and have been associated with both the pathophysiologic sequelae of infection and, more recently, with accelerated virus clearance. Here, we demonstrate that the pneumovirus pathogens, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and pneumonia virus of mice (PVM), can infect human and mouse eosinophils, respectively, and that virus infection of eosinophils elicits the release of disease-related proinflammatory mediators from eosinophils. RSV replication in human eosinophils results in the release of infectious virions and in the release of the proinflammatory mediator, interleukin-6 (IL-6). PVM replication in cultured bone marrow eosinophils (bmEos) likewise results in release of infectious virions and the proinflammatory mediators IL-6, IP-10, CCL2, and CCL3. In contrast to the findings reported in lung tissue of RSV-challenged mice, PVM replication is accelerated in MyD88 gene-deleted bmEos, whereas release of cytokines is diminished. Interestingly, exogenous IL-6 suppresses virus replication in MyD88 gene-deleted bmEos, suggesting a role for a MyD88-dependent cytokine-mediated feedback circuit in modulating this response. Taken together, our findings suggest that eosinophils are targets of virus infection and may have varied and complex contributions to the pathogenesis and resolution of pneumovirus disease.
Figures


References
-
- Hogan SP, Rosenberg HF, Moqbel R, et al. Eosinophils: biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38(5):709–750. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen EA, Taranova AG, Lee NA, Lee JJ. Eosinophils: singularly destructive effector cells or purveyors of immunoregulation? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(6):1313–1320. - PubMed
-
- Klion AD, Nutman TB. The role of eosinophils in host defense against helminth parasites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113(1):30–37. - PubMed
-
- Leckie MJ. Anti-interleukin-5 monoclonal antibodies: preclinical and clinical evidence in asthma models. Am J Respir Med. 2003;2(3):245–259. - PubMed
-
- O'Byrne PM, Inman MD, Parameswaran K. The trials and tribulations of IL-5, eosinophils, and allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:503–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

