Factors predicting and reducing mortality in patients with invasive Staphylococcus aureus disease in a developing country
- PMID: 19652705
- PMCID: PMC2714962
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006512
Factors predicting and reducing mortality in patients with invasive Staphylococcus aureus disease in a developing country
Abstract
Background: Invasive Staphylococcus aureus infection is increasingly recognised as an important cause of serious sepsis across the developing world, with mortality rates higher than those in the developed world. The factors determining mortality in developing countries have not been identified.
Methods: A prospective, observational study of invasive S. aureus disease was conducted at a provincial hospital in northeast Thailand over a 1-year period. All-cause and S. aureus-attributable mortality rates were determined, and the relationship was assessed between death and patient characteristics, clinical presentations, antibiotic therapy and resistance, drainage of pus and carriage of genes encoding Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL).
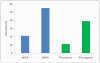
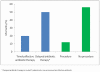
Principal findings: A total of 270 patients with invasive S. aureus infection were recruited. The range of clinical manifestations was broad and comparable to that described in developed countries. All-cause and S. aureus-attributable mortality rates were 26% and 20%, respectively. Early antibiotic therapy and drainage of pus were associated with a survival advantage (both p<0.001) on univariate analysis. Patients infected by a PVL gene-positive isolate (122/248 tested, 49%) had a strong survival advantage compared with patients infected by a PVL gene-negative isolate (all-cause mortality 11% versus 39% respectively, p<0.001). Multiple logistic regression analysis using all variables significant on univariate analysis revealed that age, underlying cardiac disease and respiratory infection were risk factors for all-cause and S. aureus-attributable mortality, while one or more abscesses as the presenting clinical feature and procedures for infectious source control were associated with survival.
Conclusions: Drainage of pus and timely antibiotic therapy are key to the successful management of S. aureus infection in the developing world. Defining the presence of genes encoding PVL provides no practical bedside information and draws attention away from identifying verified clinical risk factors and those interventions that save lives.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Nickerson EK, Wuthiekanun V, Day NP, Chaowagul W, Peacock SJ. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in rural Asia. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:70–71. - PubMed
-
- Nickerson EK, West TE, Day NP, Peacock SJ. Staphylococcus aureus disease and drug resistance in resource-limited countries in south and east Asia. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Benfield T, Espersen F, Frimodt-Moller N, Jensen AG, Larsen AR, et al. Increasing incidence but decreasing in-hospital mortality of adult Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia between 1981 and 2000. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007;13:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Das I, O'Connell N, Lambert P. Epidemiology, clinical and laboratory characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in a university hospital in UK. J Hosp Infect. 2007;65:117–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

