Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of the cervicomedullary angle in a normal adult population
- PMID: 19653012
- PMCID: PMC2899527
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-009-1112-8
Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of the cervicomedullary angle in a normal adult population
Abstract
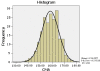
CMA values have been effectively used to evaluate the amount of BI, the brainstem and medulla compression, and the amount of postoperative decompression. However, the reliability and reproducibility of this measurement have yet to be determined. In addition, the information that is available concerning CMA values in normal individuals has been limited to small series of patients. We recruited 200 patients that underwent MR imaging of the craniovertebral junction (CVJ) for unrelated reasons. None of the patients had evidence of abnormalities at the CVJ. Two senior spine surgeons then measured the CMAs of these patients in a blind manner on three separate occasions. The CMA values ranged from 139.0 degrees to 175.5 degrees , with an average value of 158.46 degrees , and a 95% confidence interval from 144.8 degrees to 172.1 degrees . Overall, the CMA had excellent intraobserver repeatability and interobserver reliability. The CMA also had excellent intraobserver repeatability based on both the age and gender of the patients (P = 0.87 and 0.93, respectively). At the same time, the CMA also demonstrated excellent interobserver reliability based on gender (P = 0.97), while good interobserver reliability based on patients age (P = 0.23). No significant correlation between the actual CMA values and the patients' gender (P = 0.17), age (P = 0.058), or spin-echo series used (P = 0.342). This study demonstrated that CMA values obtained from midsagittal T1 MR images were a highly reliable and repeatable measurement. The data reported in this study can be used as baseline parameters for normal individuals.
Figures




References
-
- Abumi K, Ito M, Kotani Y. Cervical pedicle screw fixation. New York, NY: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003.
-
- Boden SD, Dodge LD, Bohlmann HH, Rechtine GR. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine. A long-term analysis with predictors of paralysis and recovery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75:1281–1297. - PubMed
-
- Bundschuh C, Modic MT, Kearney F, Morris R, Deal C. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine: surface-coil MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol. 1988;151:181–187. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

