The bovine mammary gland expresses multiple functional isoforms of serotonin receptors
- PMID: 19654143
- PMCID: PMC2741409
- DOI: 10.1677/JOE-09-0187
The bovine mammary gland expresses multiple functional isoforms of serotonin receptors
Abstract
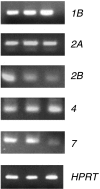
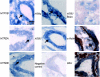
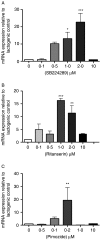
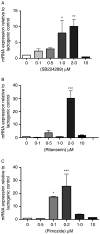
Recent studies in dairy cows have demonstrated that serotonergic ligands affect milk yield and composition. Correspondingly, serotonin (5-HT) has been demonstrated to be an important local regulator of lactational homeostasis and involution in mouse and human mammary cells. We determined the mRNA expression of bovine 5-HT receptor (HTR) subtypes in bovine mammary tissue (BMT) and used pharmacological agents to evaluate functional activities of 5-HT receptors. The mRNAs for five receptor isoforms (HTR1B, 2A, 2B, 4, and 7) were identified by conventional real-time (RT)-PCR, RT quantitative PCR, and in situ hybridization in BMT. In addition to luminal mammary epithelial cell expression, HTR4 was expressed in myoepithelium, and HTR1B, 2A, and 2B were expressed in small mammary blood vessels. Serotonin suppressed milk protein mRNA expression (alpha-lactalbumin and beta-casein mRNA) in lactogen-treated primary bovine mammary epithelial cell (BMEC) cultures. To probe the functional activities of individual receptors, caspase-3 activity and expression of alpha-lactalbumin and beta-casein were measured. Both SB22489 (1B antagonist) and ritanserin (2A antagonist) increased caspase-3 activity. Expression of alpha-lactalbumin and beta-casein mRNA levels in BMEC were stimulated by low concentrations of SB224289, ritanserin, or pimozide. These results demonstrate that there are multiple 5-HT receptor isoforms in the bovine mammary gland, and point to profound differences between serotonergic systems of the bovine mammary gland and the human and mouse mammary glands. Whereas human and mouse mammary epithelial cells express predominately the protein for the 5-HT(7) receptor, cow mammary epithelium expresses multiple receptors that have overlapping, but not identical, functional activities.
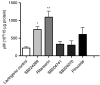
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serotonin as a homeostatic regulator of lactation.Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2012 Aug;43(2):161-70. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2012.03.006. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22608139 Review.
-
Short communication: Differences in distribution of serotonin receptor subtypes in the mammary gland of sheep, goats, and cows during lactation and involution.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Mar;102(3):2703-2707. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15328. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30639027
-
The role of native bovine alpha-lactalbumin in bovine mammary epithelial cell apoptosis and casein expression.J Dairy Res. 2008 Aug;75(3):319-25. doi: 10.1017/S0022029908003403. J Dairy Res. 2008. PMID: 18680616
-
Suppression of lactation and acceleration of involution in the bovine mammary gland by a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.J Endocrinol. 2011 Apr;209(1):45-54. doi: 10.1530/JOE-10-0452. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21307120
-
[Endogenous Serotonin and Milk Production Regulation in the Mammary Gland].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(6):829-836. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00003. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 29863055 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Exploring the contribution of mammary-derived serotonin on liver and pancreas metabolism during lactation.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 5;19(6):e0304910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304910. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38837989 Free PMC article.
-
Serotoninergic and Circadian Systems: Driving Mammary Gland Development and Function.Front Physiol. 2016 Jul 15;7:301. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00301. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27471474 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serotonin coordinates mammary metabolism in dairy cows.Physiol Rep. 2021 Apr;9(7):e14798. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14798. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33835711 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Appropriate Reference Genes for qRT-PCR Analysis of Heat-Stressed Mammary Epithelial Cells in Riverine Buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis).ISRN Biotechnol. 2013 Jan 28;2013:735053. doi: 10.5402/2013/735053. eCollection 2013. ISRN Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 25937980 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of serotonin on the cell viability of the bovine mammary alveolar cell-T (MAC-T) cell line.J Anim Sci Technol. 2022 Sep;64(5):922-936. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e50. Epub 2022 Sep 30. J Anim Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36287778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akers RM 2002 Lactation and the Mammary Gland, pp 66–87. Ames: Iowa State Press.
-
- Banes AKL, Shaw SM, Tawfik A, Patel BP, Ogbi S, Fulton D, Marrero MB. Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in vascular smooth muscle by serotonin. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology. 2005;288:805–812. - PubMed
-
- Boisgard R, Chanat E, Lavialle F, Pauloin A, Ollivier-Bousquet M. Roads taken by milk protein in mammary epithelial cells. Livestock Production Science. 2001;70:49–61.
-
- Capuco AV, Akers RM. Mammary involution in dairy animals. Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia. 1999;4:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Capuco AV, Akers RM, Smith JJ. Mammary growth in Holstein cows during the dry period: quantification of nucleic acids and histology. Journal of Dairy Science. 1997;80:477–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

