Cytokine and chemokine regulation of sensory neuron function
- PMID: 19655114
- PMCID: PMC2746245
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-79090-7_12
Cytokine and chemokine regulation of sensory neuron function
Abstract
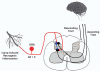
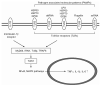
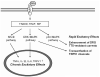
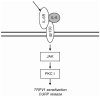
Pain normally subserves a vital role in the survival of the organism, prompting the avoidance of situations associated with tissue damage. However, the sensation of pain can become dissociated from its normal physiological role. In conditions of neuropathic pain, spontaneous or hypersensitive pain behavior occurs in the absence of the appropriate stimuli. Our incomplete understanding of the mechanisms underlying chronic pain hypersensitivity accounts for the general ineffectiveness of currently available options for the treatment of chronic pain syndromes. Despite its complex pathophysiological nature, it is clear that neuropathic pain is associated with short- and long-term changes in the excitability of sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) as well as their central connections. Recent evidence suggests that the upregulated expression of inflammatory cytokines in association with tissue damage or infection triggers the observed hyperexcitability of pain sensory neurons. The actions of inflammatory cytokines synthesized by DRG neurons and associated glial cells, as well as by astrocytes and microglia in the spinal cord, can produce changes in the excitability of nociceptive sensory neurons. These changes include rapid alterations in the properties of ion channels expressed by these neurons, as well as longer-term changes resulting from new gene transcription. In this chapter we review the diverse changes produced by inflammatory cytokines in the behavior of sensory neurons in the context of chronic pain syndromes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the immune system in neuropathic pain.Scand J Pain. 2019 Dec 18;20(1):33-37. doi: 10.1515/sjpain-2019-0138. Scand J Pain. 2019. PMID: 31730538 Review.
-
Puerarin alleviates vincristine-induced neuropathic pain and neuroinflammation via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and activation of the TGF-β/Smad pathway in rats.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt B):107060. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107060. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33049496
-
Chemokines in neuron-glial cell interaction and pathogenesis of neuropathic pain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Sep;74(18):3275-3291. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2513-1. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28389721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of Immune and Neuroinflammatory Changes Associated with Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170814. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28125674 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives in Pain Research 2014: Neuroinflammation and glial cell activation: The cause of transition from acute to chronic pain?Scand J Pain. 2015 Jan 1;6(1):3-6. doi: 10.1016/j.sjpain.2014.10.002. Scand J Pain. 2015. PMID: 29911589
Cited by
-
CCL2 and CCL3 are essential mediators of pelvic pain in experimental autoimmune prostatitis.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012 Sep 15;303(6):R580-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00240.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22814670 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TNF-α in Regulating the Exercise Pressor Reflex in Rats With Femoral Artery Occlusion.Front Physiol. 2018 Oct 15;9:1461. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01461. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30374312 Free PMC article.
-
Euphorbia bicolor (Euphorbiaceae) Latex Extract Reduces Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Orofacial Pain.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Sep 12;2019:8594375. doi: 10.1155/2019/8594375. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31612077 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilian medicinal plants with corroborated anti-inflammatory activities: a review.Pharm Biol. 2018 Dec;56(1):253-268. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1454480. Pharm Biol. 2018. PMID: 29648503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel immunocompetent model of metastatic prostate cancer-induced bone pain.Prostate. 2020 Jul;80(10):782-794. doi: 10.1002/pros.23993. Epub 2020 May 14. Prostate. 2020. PMID: 32407603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW, Viswanath V, Eid SR, Petrus MJ, Earley TJ, Patapoutian A. Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron. 2004;41:849–857. - PubMed
-
- Bhangoo S, Ren D, Miller RJ, Henry KJ, Lineswala J, Hamdouchi C, Li B, Monahan PE, Chan DM, Ripsch MS, White FA. Delayed functional expression of neuronal chemokine receptors following focal nerve demyelination in the rat: a mechanism for the development of chronic sensitization of peripheral nociceptors. Mol Pain. 2007a;3:38. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

