Age dependency of cerebral P-gp function measured with (R)-[11C]verapamil and PET
- PMID: 19655132
- PMCID: PMC3689922
- DOI: 10.1007/s00228-009-0709-5
Age dependency of cerebral P-gp function measured with (R)-[11C]verapamil and PET
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to assess the influence of age on the functional activity of the multidrug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) at the human blood-brain barrier.
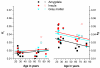
Methods: Seven young (mean age: 27 +/- 4 years) and six elderly (mean age: 69 +/- 9 years) healthy volunteers underwent dynamic (R)-[(11)C]verapamil (VPM) positron emission tomography (PET) scans and arterial blood sampling. Parametric distribution volume (DV) images were generated using Logan linearisation, and age groups were compared with statistical parametric mapping (SPM). Brain regions that SPM analysis had shown to be most affected by age were analysed by a region of interest (ROI)-based approach using a maximum probability brain atlas, before and after partial volume correction (PVC).
Results: SPM analysis revealed significant clusters of DV increases in cerebellum, temporal and frontal lobe of elderly compared to younger subjects. In the ROI-based analysis, elderly subjects showed significant DV increases in amygdala (+30%), insula (+26%) and cerebellum (+25%) before PVC, and in insula (+33%) after PVC.
Conclusions: Increased VPM DV values in the brains of elderly subjects suggest a decrease in cerebral P-gp function with increasing age.
Figures


References
-
- Löscher W, Potschka H. Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;76:22–76. - PubMed
-
- Lubberink M, Luurtsema G, van Berckel BN, Boellaard R, Toornvliet R, Windhorst AD, Franssen EJ, Lammertsma AA. Evaluation of tracer kinetic models for quantification of P-glycoprotein function using (R)-[(11)C]verapamil and PET. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:424–433. - PubMed
-
- Bartels AL, Kortekaas R, Bart J, Willemsen AT, de Klerk OL, de Vries JJ, van Oostrom JC, Leenders KL. Blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function decreases in specific brain regions with aging: A possible role in progressive neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.02.002. - PubMed
-
- Toornvliet R, van Berckel BN, Luurtsema G, Lubberink M, Geldof AA, Bosch TM, Oerlemans R, Lammertsma AA, Franssen EJ. Effect of age on functional P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain barrier measured by use of (R)-[(11)C]verapamil and positron emission tomography. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;79:540–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

