Structural and kinetic characterization of mutant human uroporphyrinogen decarboxylases
- PMID: 19656450
- PMCID: PMC2863003
Structural and kinetic characterization of mutant human uroporphyrinogen decarboxylases
Abstract
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is caused by inhibition of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (URO-D) activity in hepatocytes. Subnormal URO-D activity results in accumulation and urinary excretion of uroporphyrin and heptacarboxyl porphyrin. Heterozygosity for mutations in the URO-D gene is found in the familial form of PCT (F-PCT). Over 70 mutations of URO-D have been described but very few have been characterized structurally. Here we characterize 3 mutations in the URO-D gene found in patients with F-PCT, G318R, K297N, and D306Y. Expression of the D306Y mutation results in an insoluble recombinant protein. G318R and K297N have little effect on the structure or activity of recombinant URO-D, but the proteins display reduced stability in vitro.
Figures
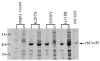
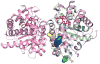
References
-
- Anderson KE, Sassa S, Bishop DF, Desnick RJ. Disorders of Heme Biosynthesis: X-linked Sideroblastic Anemia and the Porphyrias. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2001. pp. 2991–3062.
-
- Bulaj ZJ, Franklin MR, Phillips JD, Miller KL, Bergonia HA, et al. Transdermal estrogen replacement therapy in postmenopausal women previously treated for porphyria cutanea tarda. J Lab Clin Med. 2000;136:482–488. - PubMed
-
- Bulaj ZJ, Phillips JD, Ajioka RS, Franklin MR, Griffen LM, et al. Hemochromatosis genes and other factors contributing to the pathogenesis of porphyria cutanea tarda. Blood. 2000;95:1565–1571. - PubMed
-
- de Verneuil H, Grandchamp B, Nordmann Y. Some kinetic properties of human red cell uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;611:174–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
