Relationship between prepregnancy and early pregnancy uterine blood flow and resistance index
- PMID: 19657141
- PMCID: PMC2882858
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719109341843
Relationship between prepregnancy and early pregnancy uterine blood flow and resistance index
Abstract
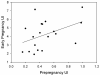
We evaluated the relationship between prepregnancy and early pregnancy uterine blood flow (UBF) and resistance index (RI). Nineteen nulliparous participants were studied during cycle day 8 + 4, and early pregnancy (13.4 + 1.6 weeks). Color Doppler ultrasound of both uterine arteries and maternal heart was performed to calculate uterine RI, volumetric UBF, and cardiac output (CO), respectively. We observed a strong negative association of uterine RI with prepregnancy UBF (r = -.82, P < .001) that weakened, but remained significant in early pregnancy (r =-.48, P = .04). Prepregnancy uterine index (UBF/CO) was significantly associated with early pregnancy uterine index; r = .48, P = .04). There was also a trend associating prepregnancy and early pregnancy volumetric UBF (r = .44, P = .068). Prepregnancy UBF may be a determinant of early pregnancy UBF and UBF may have independent value as a predictor of adverse pregnancy outcome.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenfeld CR. Distribution of cardiac output in ovine pregnancy. Am J Physiol. 1977 Mar;232(3):H231–235. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld CR, Morriss FH, Jr., Makowski EL, Meschia G, Battaglia FC. Circulatory changes in the reproductive tissues of ewes during pregnancy. Gynecol Invest. 1974;5(5-6):252–268. - PubMed
-
- Maini CL, Rosati P, Galli G, Bellati U, Bonetti MG, Moneta E. Non-invasive radioisotopic evaluation of placental blood flow. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1985;19(4):196–206. - PubMed
-
- Robson SC, Hunter S, Boys RJ, Dunlop W. Serial study of factors influencing changes in cardiac output during human pregnancy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1989 April 1;256(4):H1060–1065. 1989. - PubMed
-
- Dickey RP, Hower JF. Ultrasonographic features of uterine blood flow during the first 16 weeks of pregnancy. Hum Reprod. 1995 Sep;10(9):2448–2452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

