L1 retrotransposition in human neural progenitor cells
- PMID: 19657334
- PMCID: PMC2909034
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08248
L1 retrotransposition in human neural progenitor cells
Abstract
Long interspersed element 1 (LINE-1 or L1) retrotransposons have markedly affected the human genome. L1s must retrotranspose in the germ line or during early development to ensure their evolutionary success, yet the extent to which this process affects somatic cells is poorly understood. We previously demonstrated that engineered human L1s can retrotranspose in adult rat hippocampus progenitor cells in vitro and in the mouse brain in vivo. Here we demonstrate that neural progenitor cells isolated from human fetal brain and derived from human embryonic stem cells support the retrotransposition of engineered human L1s in vitro. Furthermore, we developed a quantitative multiplex polymerase chain reaction that detected an increase in the copy number of endogenous L1s in the hippocampus, and in several regions of adult human brains, when compared to the copy number of endogenous L1s in heart or liver genomic DNAs from the same donor. These data suggest that de novo L1 retrotransposition events may occur in the human brain and, in principle, have the potential to contribute to individual somatic mosaicism.
Figures
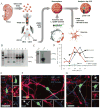
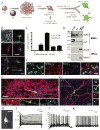


Comment in
-
Developmental biology: Jumping-gene roulette.Nature. 2009 Aug 27;460(7259):1087-8. doi: 10.1038/4601087a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19713921 No abstract available.
References
-
- Muotri AR, et al. Somatic mosaicism in neuronal precursor cells mediated by L1 retrotransposition. Nature. 2005;435(7044):903–910. - PubMed
-
- Tang Y, Nyengaard JR, De Groot DM, Gundersen HJ. Synapse. 3. Vol. 41. New York, N.Y: 2001. Total regional and global number of synapses in the human brain neocortex; pp. 258–273. - PubMed
-
- Moran JV, et al. High frequency retrotransposition in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1996;87(5):917–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

