Human disease-drug network based on genomic expression profiles
- PMID: 19657382
- PMCID: PMC2715883
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006536
Human disease-drug network based on genomic expression profiles
Abstract
Background: Drug repositioning offers the possibility of faster development times and reduced risks in drug discovery. With the rapid development of high-throughput technologies and ever-increasing accumulation of whole genome-level datasets, an increasing number of diseases and drugs can be comprehensively characterized by the changes they induce in gene expression, protein, metabolites and phenotypes.
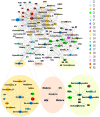
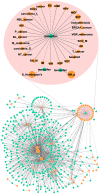
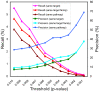
Methodology/principal findings: We performed a systematic, large-scale analysis of genomic expression profiles of human diseases and drugs to create a disease-drug network. A network of 170,027 significant interactions was extracted from the approximately 24.5 million comparisons between approximately 7,000 publicly available transcriptomic profiles. The network includes 645 disease-disease, 5,008 disease-drug, and 164,374 drug-drug relationships. At least 60% of the disease-disease pairs were in the same disease area as determined by the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) disease classification tree. The remaining can drive a molecular level nosology by discovering relationships between seemingly unrelated diseases, such as a connection between bipolar disorder and hereditary spastic paraplegia, and a connection between actinic keratosis and cancer. Among the 5,008 disease-drug links, connections with negative scores suggest new indications for existing drugs, such as the use of some antimalaria drugs for Crohn's disease, and a variety of existing drugs for Huntington's disease; while the positive scoring connections can aid in drug side effect identification, such as tamoxifen's undesired carcinogenic property. From the approximately 37K drug-drug relationships, we discover relationships that aid in target and pathway deconvolution, such as 1) KCNMA1 as a potential molecular target of lobeline, and 2) both apoptotic DNA fragmentation and G2/M DNA damage checkpoint regulation as potential pathway targets of daunorubicin.
Conclusions/significance: We have automatically generated thousands of disease and drug expression profiles using GEO datasets, and constructed a large scale disease-drug network for effective and efficient drug repositioning as well as drug target/pathway identification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Augen J. Industrialized molecular biology, information biotechnology, and the blockbuster drug model–alive and well at age 50. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7:S157–S159. - PubMed
-
- Yildirim MA, Goh KI, Cusick ME, Barabasi AL, Vidal M. Drug-target network. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1119–1126. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1110–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

