Noninvasive, in vivo imaging of the mouse brain using photoacoustic microscopy
- PMID: 19657402
- PMCID: PMC2719465
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3116134
Noninvasive, in vivo imaging of the mouse brain using photoacoustic microscopy
Abstract
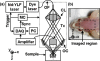
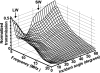
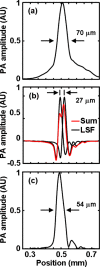
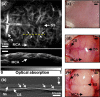
Noninvasive, high resolution imaging of mouse brain activity is poised to provide clinically translatable insights into human neurological disease progression. Toward noninvasive imaging of brain activity through the hemodynamic response, the dark-field photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) technique was enhanced to image the cortex vasculature of the mouse brain in vivo using endogenous hemoglobin contrast. Specifically, the PAM system was redesigned to efficiently collect photoacoustic waves originating from cortical vessels, providing high (70 mum lateral and 54 mum axial) resolution images of the mouse brain vasculature with a contrast-to-noise ratio of 25 dB. These findings confirm the efficacy of PAM to noninvasively image vascular structures in the mouse brain and the potential to image mouse brain function by tracking the hemodynamic response.
Figures
References
-
- Hafezparast M., Ahmad-Annuar A., Wood N. W., Tabrizi S. J., and Fisher E. M., Lancet Neurol. 1, 215 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Xu M. H. and Wang L. V., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 041101 (2006).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
