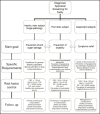
Key priorities in managing glucose control in older people with diabetes
- PMID: 19657551
- PMCID: PMC12275583
- DOI: 10.1007/s12603-009-0198-3
Key priorities in managing glucose control in older people with diabetes
Abstract
Older people with diabetes represent a major and increasing proportion of our elderly population and their care requires better organisation. Targets for risk factor control and pathways of care must be adjusted to the subject's general health status. It is thus advisable to screen for frailty. We have carried out a detailed literature review of the studies published on diabetes in older people since 1990. Studies were considered if they included groups or subgroups of diabetic patients > 65 years old. This review discusses the elaboration of general targets for care, the approach to risk factor control, the screening and the specific prevention or management of complications, the integration of geriatric concepts in diabetes care and the specificity of education with respect to frailty status.
Figures
Comment in
-
Effective clinical practice for older people with type 2 diabetes. Glucose regulation is important but other strategies also need to be included.J Nutr Health Aging. 2010 Jan;14(1):3-4. doi: 10.1007/s12603-010-0001-5. J Nutr Health Aging. 2010. PMID: 20082046 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fagot-Campagna A., Bourdel-Marchasson I., Simon D. Burden of diabetes in an aging population: prevalence, incidence, mortality, characteristics and quality of care. Diabetes & metabolism. 2005;31(Spec2):5S35–35S52. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes U. Diabetes in the UK 2004. Diabetes, UK; London, England: 2004.
-
- Névanen S., Tambekou J., Fosse S., et al. Caractéristiques et état de santé des personnes diabétiques âgées et leur prise en charge médicale, étude Entred 2001. Bulletin Epidemiologique Hebdomadaire. 2005;12-13:51–52.
-
- Ubink-Veltmaat L.J., Bilo H.J., Groenier K.H., et al. Prevalence, incidence and mortality of type 2 diabetes mellitus revisited: a prospective population-based study in The Netherlands (ZODIAC-1) Eur J Epidemiol. 2003;18:793–800. 10.1023/A:1025369623365 12974556. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bourdel-Marchasson I., Helmer C., Fagot-Campagna A., Dehail P., Joseph P.A. Disability and quality of life in elderly people with diabetes. Diabetes & metabolism. 2007;33(Suppl1):S66–S74. 10.1016/S1262-3636(07)80058-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical