Stringent regulation of complement lectin pathway C3/C5 convertase by C4b-binding protein (C4BP)
- PMID: 19660812
- PMCID: PMC2770428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.07.006
Stringent regulation of complement lectin pathway C3/C5 convertase by C4b-binding protein (C4BP)
Abstract
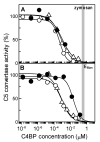
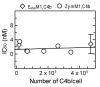
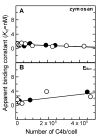
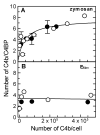
The complement lectin pathway, an essential component of the innate immune system, is geared for rapid recognition of infections as each C4b deposited via this pathway is capable of forming a C3/C5 convertase. In the present study, role of C4b-binding protein (C4BP) in regulating the lectin pathway C3/C5 convertase assembled on zymosan and sheep erythrocytes coated with mannan (E(Man)) was examined. While the C4BP concentration for inhibiting 50% (IC(50)) formation of surface-bound C3 convertase on the two surfaces was similar to that obtained for the soluble C3 convertase (1.05nM), approximately 3- and 41-fold more was required to inhibit assembly of the C5 convertase on zymosan (2.81nM) and E(Man) (42.66nM). No difference in binding interactions between C4BP and surface-bound C4b alone or in complex with C3b was observed. Increasing the C4b density on zymosan (14,000-431,000 C4b/Zym) increased the number of C4b bound per C4BP from 2.87 to 8.23 indicating that at high C4b density all seven alpha-chains of C4BP are engaged in C4b-binding. In contrast, the number of C4b bound per C4BP remained constant (3.79+/-0.60) when the C4b density on E(Man) was increased. The data also show that C4BP regulates assembly and decay of the lectin pathway C3/C5 convertase more stringently than the classical pathway C3/C5 convertase because of a approximately 7- to 13-fold greater affinity for C4b deposited via the lectin pathway than the classical pathway. C4BP thus regulates efficiently the four times greater potential of the lectin pathway than the classical pathway in generating the C3/C5 convertase and hence production of pro-inflammatory products, which are required to fight infections but occasionally cause pathological inflammatory reactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of complement component C5: comparison of C5 convertases of the lectin pathway and the classical pathway of complement.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 21;283(12):7853-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707591200. Epub 2008 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18204047
-
Role of the C3b-binding site on C4b-binding protein in regulating classical pathway C5 convertase.Mol Immunol. 2007 Feb;44(6):1105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.07.282. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 16979240
-
Formation of high affinity C5 convertase of the classical pathway of complement.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 3;278(40):38476-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307017200. Epub 2003 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12878586
-
The Complement System and C4b-Binding Protein: A Focus on the Promise of C4BPα as a Biomarker to Predict Clopidogrel Resistance.Mol Diagn Ther. 2024 Mar;28(2):189-199. doi: 10.1007/s40291-023-00691-w. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Mol Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38261250 Review.
-
Structure/function of C5 convertases of complement.Int Immunopharmacol. 2001 Mar;1(3):415-22. doi: 10.1016/s1567-5769(00)00039-4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11367526 Review.
Cited by
-
Is the COVID-19 thrombotic catastrophe complement-connected?J Thromb Haemost. 2020 Nov;18(11):2812-2822. doi: 10.1111/jth.15050. Epub 2020 Sep 18. J Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 32762081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Proteomic Profiling of a Group of Anxious Dogs by LC-MS/MS: A Case-Control Study.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2025 Jul;19(4):e70014. doi: 10.1002/prca.70014. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2025. PMID: 40614171 Free PMC article.
-
A computational and experimental study of the regulatory mechanisms of the complement system.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Jan 20;7(1):e1001059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001059. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21283780 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of developmental lead exposure on splenic factors.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 1;247(2):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.06.003. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20542052 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Reveals a Role for the Complement System in Medullary Sponge Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 5;20(21):5517. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215517. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31694344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aittoniemi J, Miettinen A, Laippala P, Isolauri E, Viikari J, Ruuska T, Soppi E. Age-dependent variation in the serum concentration of mannan-binding protein. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:906–909. - PubMed
-
- Blom AM, Webb J, Villoutreix BO, Dahlbäck B. A cluster of positively charged amino acids in the C4BP α-chain is crucial for C4b binding and factor I cofactor function. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19237–19245. - PubMed
-
- Blom AM, Kask L, Dahlbäck B. Structural requirements for the complement regulatory activities of C4BP. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:27136–27144. - PubMed
-
- Blom AM. Structural and functional studies of complement inhibitor C4b-binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:978–982. - PubMed
-
- Blom AM, Kask L, Dahlbäck B. CCP1-4 of the C4b-binding protein α-chain are required for factor I mediated cleavage of complement factor C3b. Mol Immunol. 2003;39:547–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

