Role of substance P signaling in enhanced nociceptive sensitization and local cytokine production after incision
- PMID: 19660865
- PMCID: PMC2746201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.06.037
Role of substance P signaling in enhanced nociceptive sensitization and local cytokine production after incision
Abstract
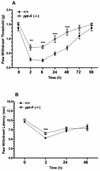
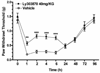
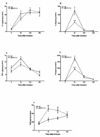
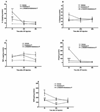
Substance P (SP) signaling facilitates nociceptive sensitization in various inflammatory and chronic pain models and we postulated that SP signaling might also contribute to the development of post-incisional hyperalgesia. These studies used mice with a deletion of the pre-protachykinin A gene (ppt-A(-/-)) which codes for SP to determine the role of SP signaling in post-incisional pain and in the increased cytokine and nerve growth factor (NGF) expression observed in the incised skin. SP deficient ppt-A(-/-) mice displayed reduced mechanical allodynia and heat hyperalgesia compared to the wild-type (wt) mice at all post-incision time points, despite similar baseline values (p<0.001). Furthermore, the NK-1 receptor antagonist LY303870 attenuated mechanical allodynia produced by incision in the wt mice (p<0.001). Incision also up-regulated IL-6, TNF-alpha and KC levels but not IL-1beta after 2h in the wt mice skin. However, ppt-A(-/-) mice had more skin NGF levels 2h post-incision. Subcutaneous hind paw SP injection produced acute and transient elevations of IL-1beta, IL-6, and KC but modest elevations in TNF-alpha levels in the wt mice. Systemic LY303870 reversed the SP-induced elevations of these cytokines. Hind paw injection of IL-6 and NGF dose dependently produced less mechanical allodynia in the ppt-A(-/-) compared to wt mice. Additionally, SP produced mechanical allodynia in a dose-dependent fashion in wt mice. Therefore, SP supports nociceptive sensitization after hind paw incision and potentially participates directly in modulating the intensity of inflammatory response in peri-incisional tissue.
Figures

References
-
- Akaishi S, Ogawa R, Hyakusoku H. Keloid and hypertrophic scar: neurogenic inflammation hypotheses. Med Hypotheses. 2008;71(1):32–38. - PubMed
-
- Amann R, Schuligoi R. Beta adrenergic inhibition of capsaicin-induced, NK1 receptor-mediated nerve growth factor biosynthesis in rat skin. Pain. 2004;112(1–2):76–82. - PubMed
-
- Amann R, Schuligoi R, Herzeg G, Donnerer J. Intraplantar injection of nerve growth factor into the rat hind paw: local edema and effects on thermal nociceptive threshold. Pain. 1996;64(2):323–329. - PubMed
-
- Andreev N, Dimitrieva N, Koltzenburg M, McMahon SB. Peripheral administration of nerve growth factor in the adult rat produces a thermal hyperalgesia that requires the presence of sympathetic post-ganglionic neurones. Pain. 1995;63(1):109–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

