Effects of a single dose of N-carbamylglutamate on the rate of ureagenesis
- PMID: 19660971
- PMCID: PMC2784258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.07.010
Effects of a single dose of N-carbamylglutamate on the rate of ureagenesis
Erratum in
- Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Apr;99(4):440
Abstract
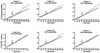
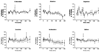
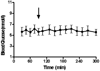
We studied the effect on ureagenesis of a single dose of N-carbamylglutamate (NCG) in healthy young adults who received a constant infusion (300 min) of NaH(13)CO(3). Isotope ratio-mass spectrometry was used to measure the appearance of label in [(13)C]urea. At 90 min after initiating the H(13)CO3-infusion each subject took a single dose of NCG (50 mg/kg). In 5/6 studies the administration of NCG increased the formation of [(13)C]urea. Treatment with NCG significantly diminished the concentration of blood alanine, but not that of glutamine or arginine. The blood glucose concentration was unaffected by NCG administration. No untoward side effects were observed. The data indicate that treatment with NCG stimulates ureagenesis and could be useful in clinical settings of acute hyperammonemia of various etiologies.
Figures

References
-
- Hall LM, Metzenberg RL, Cohen PP. Isolation and characterization of a naturally occurring cofactor of carbamyl phosphate biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958;230:1013–1021. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann C, Colombo JP, Jaggi K. N-acetylglutamate synthetase (NAGS) deficiency: diagnosis, clinical observations and treatment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;153:39–45. - PubMed
-
- Schubiger G, Bachmann C, Barben P, Colombo JP, Tonz O, Schupbach D. N-acetylglutamate synthetase deficiency: diagnosis, management and follow-up of a rare disorder of ammonia detoxication. Eur J Pediatr. 1991;150:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Caldovic L, Morizono H, Panglao MG, Cheng SF, Packman S, Tuchman M. Null mutations in the N-acetylglutamate synthase gene associated with acute neonatal disease and hyperammonemia. Hum Genet. 2003;112:364–368. - PubMed
-
- Caldovic L, Morizono H, Panglao MG, Lopez GY, Shi D, Summar ML, Tuchman M. Late onset N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency caused by hypomorphic alleles. Hum Mutat. 2005;25:293–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK064913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK53761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK053761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD061221/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR00240/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR019453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD058567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR019453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK47870/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000240/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD26979/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD058567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD026979/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

