The neurobiological toll of child abuse and neglect
- PMID: 19661133
- PMCID: PMC6492037
- DOI: 10.1177/1524838009339758
The neurobiological toll of child abuse and neglect
Abstract
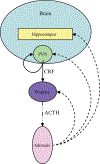
Exposure to interpersonal violence or abuse affects the physical and emotional well-being of affected individuals. In particular, exposure to trauma during development increases the risk of psychiatric and other medical disorders beyond the risks associated with adult violence exposure. Alterations in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a major mediating pathway of the stress response, contribute to the long-standing effects of early life trauma. Although early life trauma elevates the risk of psychiatric and medical disease, not all exposed individuals demonstrate altered HPA axis physiology, suggesting that genetic variation influences the consequences of trauma exposure. In addition, the effects of abuse may extend beyond the immediate victim into subsequent generations as a consequence of epigenetic effects transmitted directly to offspring and/or behavioral changes in affected individuals. Recognition of the biological consequences and transgenerational impact of violence and abuse has critical importance for both disease research and public health policy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Childhood emotional abuse and neglect as predictors of psychological and physical symptoms in women presenting to a primary care practice.Child Abuse Negl. 2003 Nov;27(11):1247-58. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2003.05.001. Child Abuse Negl. 2003. PMID: 14637300
-
Psychiatric diagnosis as a risk marker for victimization in a national sample of children.J Interpers Violence. 2009 Apr;24(4):636-52. doi: 10.1177/0886260508317197. Epub 2008 Apr 29. J Interpers Violence. 2009. PMID: 18445831
-
Abuse-related posttraumatic stress disorder and alterations of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in women with chronic pelvic pain.Psychosom Med. 1998 May-Jun;60(3):309-18. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199805000-00017. Psychosom Med. 1998. PMID: 9625218
-
Risk and resilience: genetic and environmental influences on development of the stress response.Depress Anxiety. 2009;26(11):984-92. doi: 10.1002/da.20605. Depress Anxiety. 2009. PMID: 19750552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress and development: behavioral and biological consequences.Dev Psychopathol. 2001 Summer;13(3):473-89. doi: 10.1017/s0954579401003042. Dev Psychopathol. 2001. PMID: 11523844 Review.
Cited by
-
A 3-year retrospective study of 866 children and adolescent outpatients followed in the Nice Pediatric Psychotrauma Center created after the 2016 mass terror attack.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 8;13:1010957. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1010957. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36569628 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Osteopontin Expression in Abusive Head Trauma Compared with Other Causes of Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury.J Pediatr. 2020 Dec;227:170-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.06.080. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32622673 Free PMC article.
-
Differential methylation of genes in the medial prefrontal cortex of developing and adult rats following exposure to maltreatment or nurturing care during infancy.Dev Neurosci. 2013;35(4):306-16. doi: 10.1159/000350716. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23751776 Free PMC article.
-
The mediating role of anxiety between child abuse and pain among a sample of Lebanese adults.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16559. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01689-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360660 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction as a neurobiological correlate of emotion dysregulation in adolescent suicide.World J Pediatr. 2012 Aug;8(3):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s12519-012-0358-0. Epub 2012 Aug 12. World J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22886191 Review.
References
-
- Arato M, Banki CM, Bissette G, & Nemeroff CB (1989). Elevated CSF CRF in suicide victims. Biological Psychiatry, 25, 355–359. - PubMed
-
- Arborelius L, Owens MJ, Plotsky PM, & Nemeroff CB (1999). The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in depression and anxiety disorders. The Journal of Endocrinology, 160, 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Armanini MP, Hutchins C, Stein BA, & Sapolsky RM (1990). Glucocorticoid endangerment of hippocampal neurons is NMDA-receptor dependent. Brain Res, 532(1–2), 7–12. - PubMed
-
- Armony JL, Corbo V, Clement MH, & Brunet A (2005). Amygdala response in patients with acute PTSD to masked and unmasked emotional facial expressions. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162, 1961–1963. - PubMed
SUGGESTED READINGS
-
- Nemeroff CB, Bremner JD, Foa EB, Mayberg HS, North CS, & Stein MB (2006). Posttraumatic stress disorder: A state-of-the-science review. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 40, 1–21. - PubMed
-
- Heim C, Newport DJ, Mletzko T, Miller AH, & Nemeroff CB (2008). The link between childhood trauma and depression: Insights from the HPA axis studies in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 33, 693–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

