Regulation of monoamine oxidase A by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome
- PMID: 19661285
- PMCID: PMC2775015
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-139097
Regulation of monoamine oxidase A by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome
Abstract
Monoamine oxidase A (MAO A), encoded by the X chromosome, catalyzes the oxidative deamination of monoamine neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, and plays a critically important role in brain development and functions. Abnormal MAO A activity has been implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, autism, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, which show sexual dimorphism. However, the molecular basis for these disease processes is unclear. Recently, we found that MAO A was a putative target gene directly regulated by a transcription factor encoded by the sex-determining region Y (SRY) gene located on the Y chromosome. We demonstrated that SRY activates both MAO A-promoter and catalytic activities in a human male neuroblastoma BE(2)C cell line. A functional SRY-binding site in the MAO A core promoter was identified and validated by electrophoretic mobility shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses. Coimmunoprecipitation and ChIP assays showed that SRY and Sp1 form a transcriptional complex and synergistically activate MAO A transcription. This is the first study demonstrating that the Y-encoded transcription factor SRY is capable of regulating an X-located gene, suggesting a novel molecular mechanism for sexual dimorphism in neural development, brain functions, and initiation/progression of neural disorders associated with MAO A dysfunction.
Figures
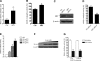


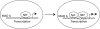
References
-
- Lan N C, Heinzmann C, Gal A, Klisak I, Orth U, Lai E, Grimsby J, Sparkes R S, Mohandas T, Shih J C. Human monoamine oxidase A and B genes map to Xp 11.23 and are deleted in a patient with Norrie disease. Genomics. 1989;4:552–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

