Moderately decreased cholesterol absorption rates are associated with a large atheroprotective effect
- PMID: 19661480
- PMCID: PMC2766672
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.194605
Moderately decreased cholesterol absorption rates are associated with a large atheroprotective effect
Abstract
Objective: Human treatment with ezetimibe results in a moderate 50% to 54% decrease in cholesterol absorption and a 15% to 20% decrease in plasma LDL-cholesterol levels; nevertheless, the efficacy of ezetimibe therapy has been recently challenged by the ENHANCE trial. We examined the efficacy of a moderate decrease in cholesterol absorption in preventing atherosclerosis formation in the mouse.
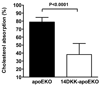
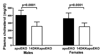
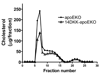
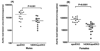
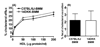
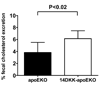
Methods and results: Congenic 14DKK animals, consisting of a castaneus (CASA/Rk) chromosome 14 interval introgressed onto the C57BL/6J background, displayed a moderate decrease in cholesterol absorption rates. The effect of moderately decreased absorption on atherosclerosis formation was determined in 14DKK apolipoprotein E knockouts (14DKK-apoEKO). When compared to chow diet-fed control apoEKO mice, congenic 14DKK-apoEKO displayed a moderate 41% decrease in cholesterol absorption rates, 30% to 37% decrease in plasma cholesterol levels, and a 70% decrease in atherosclerosis formation. Studies on cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) from 14DKK bone marrow-derived macrophages rejected a 14DKK interval-dependent atheroprotective effects that operate in macrophages. In contrast, 14DKK-apoEKO congenics were characterized by a 60% increase in RCT from peripheral tissue macrophages.
Conclusions: These studies strongly suggest that moderately decreased cholesterol absorption rates result in a large atheroprotective effect attributable to a decrease in plasma cholesterol levels and an increase in RCT from peripheral tissue macrophages.
Figures
References
-
- Sudhop T, Lutjohann D, Kodal A, Igel M, Tribble DL, Shah S, Perevozskaya I, von Bergmann K. Inhibition of intestinal cholesterol absorption by ezetimibe in humans. Circulation. 2002;106:1943–1948. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Giugliano RP, Blazing MA, Harrington RA, Peterson JL, Sisk CM, Strony J, Musliner TA, McCabe CH, Veltri E, Braunwald E, Califf RM. Rationale and design of IMPROVE-IT (IMProved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial): comparison of ezetimbe/simvastatin versus simvastatin monotherapy on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Am Heart J. 2008;156:826–832. - PubMed
-
- Peto R, Emberson J, Landray M, Baigent C, Collins R, Clare R, Califf R. Analyses of cancer data from three ezetimibe trials. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1357–1366. - PubMed
-
- Kastelein JJ, Akdim F, Stroes ES, Zwinderman AH, Bots ML, Stalenhoef AF, Visseren FL, Sijbrands EJ, Trip MD, Stein EA, Gaudet D, Duivenvoorden R, Veltri EP, Marais AD, de Groot E. Simvastatin with or without ezetimibe in familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1431–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

