A key role for Ctf4 in coupling the MCM2-7 helicase to DNA polymerase alpha within the eukaryotic replisome
- PMID: 19661920
- PMCID: PMC2760104
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.226
A key role for Ctf4 in coupling the MCM2-7 helicase to DNA polymerase alpha within the eukaryotic replisome
Abstract
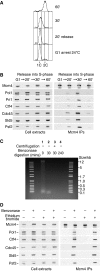
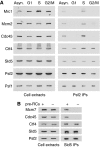
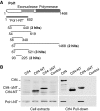
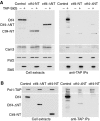
The eukaryotic replisome is a crucial determinant of genome stability, but its structure is still poorly understood. We found previously that many regulatory proteins assemble around the MCM2-7 helicase at yeast replication forks to form the replisome progression complex (RPC), which might link MCM2-7 to other replisome components. Here, we show that the RPC associates with DNA polymerase alpha that primes each Okazaki fragment during lagging strand synthesis. Our data indicate that a complex of the GINS and Ctf4 components of the RPC is crucial to couple MCM2-7 to DNA polymerase alpha. Others have found recently that the Mrc1 subunit of RPCs binds DNA polymerase epsilon, which synthesises the leading strand at DNA replication forks. We show that cells lacking both Ctf4 and Mrc1 experience chronic activation of the DNA damage checkpoint during chromosome replication and do not complete the cell cycle. These findings indicate that coupling MCM2-7 to replicative polymerases is an important feature of the regulation of chromosome replication in eukaryotes, and highlight a key role for Ctf4 in this process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
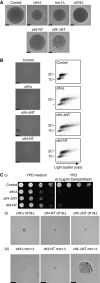
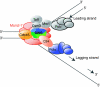
References
-
- Aguilera A, Gomez-Gonzalez B (2008) Genome instability: a mechanistic view of its causes and consequences. Nat Rev Genet 9: 204–217 - PubMed
-
- Alcasabas AA, Osborn AJ, Bachant J, Hu F, Werler PJ, Bousset K, Furuya K, Diffley JF, Carr AM, Elledge SJ (2001) Mrc1 transduces signals of DNA replication stress to activate Rad53. Nat Cell Biol 3: 958–965 - PubMed
-
- Aparicio OM, Weinstein DM, Bell SP (1997) Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: redistribution of MCM complexes and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell 91: 59–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

