HIV-1 matrix dependent membrane targeting is regulated by Gag mRNA trafficking
- PMID: 19662089
- PMCID: PMC2717210
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006551
HIV-1 matrix dependent membrane targeting is regulated by Gag mRNA trafficking
Abstract
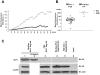
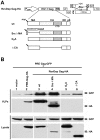
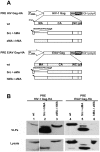
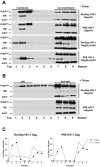
Retroviral Gag polyproteins are necessary and sufficient for virus budding. Productive HIV-1 Gag assembly takes place at the plasma membrane. However, little is known about the mechanisms by which thousands of Gag molecules are targeted to the plasma membrane. Using a bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay, we recently reported that the cellular sites and efficiency of HIV-1 Gag assembly depend on the precise pathway of Gag mRNA export from the nucleus, known to be mediated by Rev. Here we describe an assembly deficiency in human cells for HIV Gag whose expression depends on hepatitis B virus (HBV) post-transcriptional regulatory element (PRE) mediated-mRNA nuclear export. PRE-dependent HIV Gag expressed well in human cells, but assembled with slower kinetics, accumulated intracellularly, and failed to associate with a lipid raft compartment where the wild-type Rev-dependent HIV-1 Gag efficiently assembles. Surprisingly, assembly and budding of PRE-dependent HIV Gag in human cells could be rescued in trans by co-expression of Rev-dependent Gag that provides correct membrane targeting signals, or in cis by replacing HIV matrix (MA) with other membrane targeting domains. Taken together, our results demonstrate deficient membrane targeting of PRE-dependent HIV-1 Gag and suggest that HIV MA function is regulated by the trafficking pathway of the encoding mRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

