Megaprosthesis versus Condyle-sparing intercalary allograft: distal femoral sarcoma
- PMID: 19662462
- PMCID: PMC2758955
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-009-1024-2
Megaprosthesis versus Condyle-sparing intercalary allograft: distal femoral sarcoma
Abstract
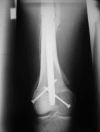
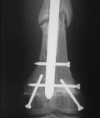
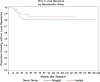
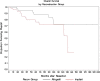
Although functionally appealing in preserving the native knee, the condyle-sparing intercalary allograft of the distal femur may be associated with a higher risk of tumor recurrence and endoprosthetic replacement for malignant distal femoral bone tumors. We therefore compared the risk of local tumor recurrence between patients in these two types of reconstruction groups. We retrospectively reviewed 85 patients (mean age, 22 years; range, 4-82 years), 38 (45%) of whom had a condyle-sparing allograft and 47 (55%) of whom had endoprostheses. The minimum followup for both groups was 2 years (mean, 7 years; range, 2-19 years). Local recurrences occurred in 11% (five of 47) of the patients having implants versus 18% (seven of 38) of the patients having allografts. Using time to local recurrence as an end point, the Kaplan-Meier survivorship of the implant group was similar to that of the condyle-sparing allograft group at 2, 5, and 10 years (93% versus 87% at 2 years, 87% versus 81% at 5 years, and 87% versus 81% at 10 years, respectively). The condyle-sparing allograft procedure offers the potential advantage of retaining the native knee in a young patient population while incurring no greater risk of local recurrence as those offered the endoprosthetic procedure.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures

References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7822356', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7822356/'}]}
- Alman BA, De Bari A, Krajbich JI. Massive allografts in the treatment of osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:54–64. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00003086-200207000-00028', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200207000-00028'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12072766', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12072766/'}]}
- Bickels J, Wittig JC, Kollender Y, Henshaw RM, Kellar-Graney KL, Meller I, Malawer MM. Distal femur resection with endoprosthetic reconstruction: a long-term followup study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;400:225–235. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3818760', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3818760/'}]}
- Bradish CF, Kemp HB, Scales JT, Wilson JN. Distal femoral replacement by custom-made prostheses. Clinical follow-up and survivorship analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69:276–284. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8194221', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8194221/'}]}
- Brien E, Terek R, Healey J, Lane J. Allograft reconstruction after proximal tibial resection for bone tumors. An analysis of function and outcome comparing allograft and prosthetic reconstructions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;303:116–127. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1884559', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1884559/'}]}
- Dubousset J, Missenard G, Kalifa C. Management of osteogenic sarcoma in children and adolescents. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;270:52–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

